Trilaciclib Prior to Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Final Efficacy and Subgroup Analysis from a Randomized Phase II Study
- PMID: 34887261
- PMCID: PMC9377748
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-2272
Trilaciclib Prior to Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Final Efficacy and Subgroup Analysis from a Randomized Phase II Study
Abstract
Purpose: We report final antitumor efficacy results from a phase II study of trilaciclib, an intravenous cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor, administered prior to gemcitabine plus carboplatin (GCb) in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (NCT02978716).
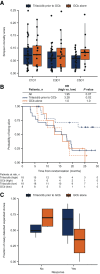
Patients and methods: Patients were randomized (1:1:1) to group 1 [GCb (days 1, 8); n = 34], group 2 [trilaciclib prior to GCb (days 1, 8); n = 33], or group 3 [trilaciclib (days 1, 8) and trilaciclib prior to GCb (days 2, 9); n = 35]. Subgroup analyses were performed according to CDK4/6 dependence, level of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression, and RNA-based immune signatures using proportional hazards regression. T-cell receptor (TCR) β CDR3 regions were amplified and sequenced to identify, quantify, and compare the abundance of each unique TCRβ CDR3 at baseline and on treatment.
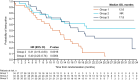
Results: Median overall survival (OS) was 12.6 months in group 1, not reached in group 2 (HR = 0.31; P = 0.0016), 17.8 months in group 3 (HR = 0.40; P = 0.0004), and 19.8 months in groups 2 and 3 combined (HR = 0.37; P < 0.0001). Efficacy outcomes were comparable regardless of cancer CDK4/6 dependence status and immune signatures. Administering trilaciclib prior to GCb prolonged OS irrespective of PD-L1 status but had greater benefit in the PD-L1-positive population. T-cell activation was enhanced in patients receiving trilaciclib.
Conclusions: Administering trilaciclib prior to GCb enhanced antitumor efficacy, with significant improvements in OS. Efficacy outcomes in immunologic subgroups and enhancements in T-cell activation suggest these improvements may be mediated via immunologic mechanisms.
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:4429–34. - PubMed
-
- Twelves C, Jove M, Gombos A, Awada A. Cytotoxic chemotherapy: still the mainstay of clinical practice for all subtypes metastatic breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2016;100:74–87. - PubMed
-
- Cortes J, Cescon DW, Rugo HS, Nowecki Z, Im SA, Yusof MM, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-355): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial. Lancet 2020;396:1817–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

