Changes in respiratory diseases in South Korea during the COVID-19 pandemic: an interrupted time series study
- PMID: 34887303
- PMCID: PMC8662586
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2021-006912
Changes in respiratory diseases in South Korea during the COVID-19 pandemic: an interrupted time series study
Abstract
Introduction: In South Korea, non-pharmaceutical interventions such as mask-wearing, hand washing and social distancing were strictly implemented to prevent the spread of COVID-19 after a national crisis alert was raised to the highest level early in the pandemic (23 February 2020). We aimed to investigate changes in the occurrence of respiratory diseases at the national level after the COVID-19 outbreak.
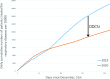
Methods: The study period was from 1 January to 1 August 2019 (213 days) and from 1 January to 31 July 2020 (213 days). Based on the National Health Insurance Service data, we analysed changes in the numbers of patients treated for respiratory diseases. The changes in the numbers of individuals using public transportation and visiting the theatre were investigated to assess the effect of social distancing after the national crisis alert was raised. Differences in daily cumulative numbers (DDCNs) in 2020 were calculated as follows: (daily cumulative number in 2020)-(cumulative number for that day in 2019). A change over time in DDCNs of <0 was taken as indication that the numbers decreased from 2019 to 2020. Segmented regression analyses were performed using generalised least squares method to identify changes in trends of DDCNs of patients treated for respiratory diseases and individuals using public transportation and visiting the theatre.
Results: After the national crisis alert was raised to the highest level, DDCNs of patients treated for respiratory diseases, individuals using public transportation, and those visiting the theatre exhibited a significant daily decline by 53.18 per 10 000 inhabitants (95% CI -65.86 to -40.49), 48.19 per 1000 inhabitants (95% CI -62.05 to -34.32) and 25.30 per 5000 inhabitants (95% CI -36.30 to -14.30), respectively, compared with before the national crisis alert was raised.
Conclusion: Non-pharmaceutical interventions to prevent the spread of COVID-19 significantly reduce the incidence of respiratory diseases.
Keywords: COVID-19; respiratory infections.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Ladegaard MB, Stage V. [Hand-hygiene and sickness among small children attending day care centers. An intervention study]. Ugeskr Laeger 1999;161:4396–400. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
