AMPK modulation ameliorates dominant disease phenotypes of CTRP5 variant in retinal degeneration
- PMID: 34887495
- PMCID: PMC8660775
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02872-x
AMPK modulation ameliorates dominant disease phenotypes of CTRP5 variant in retinal degeneration
Abstract
Late-onset retinal degeneration (L-ORD) is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a missense substitution in CTRP5. Distinctive clinical features include sub-retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) deposits, choroidal neovascularization, and RPE atrophy. In induced pluripotent stem cells-derived RPE from L-ORD patients (L-ORD-iRPE), we show that the dominant pathogenic CTRP5 variant leads to reduced CTRP5 secretion. In silico modeling suggests lower binding of mutant CTRP5 to adiponectin receptor 1 (ADIPOR1). Downstream of ADIPOR1 sustained activation of AMPK renders it insensitive to changes in AMP/ATP ratio resulting in defective lipid metabolism, reduced Neuroprotectin D1(NPD1) secretion, lower mitochondrial respiration, and reduced ATP production. These metabolic defects result in accumulation of sub-RPE deposits and leave L-ORD-iRPE susceptible to dedifferentiation. Gene augmentation of L-ORD-iRPE with WT CTRP5 or modulation of AMPK, by metformin, re-sensitize L-ORD-iRPE to changes in cellular energy status alleviating the disease cellular phenotypes. Our data suggests a mechanism for the dominant behavior of CTRP5 mutation and provides potential treatment strategies for L-ORD patients.
© 2021. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


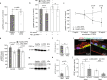
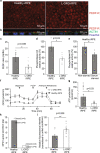

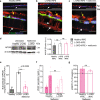
References
-
- Soumplis V, et al. Phenotypic findings in C1QTNF5 retinopathy (late-onset retinal degeneration) Acta Ophthalmol. 2013;91:e191–e195. - PubMed
-
- Borooah S, Collins C, Wright A, Dhillon B. Republished review. [corrected] Late-onset retinal macular degeneration: clinical insights into an inherited retinal degeneration. Postgrad. Med. J. 2009;85:495–500. - PubMed
-
- Ramtohul P, Gascon P, Matonti F. Choroidal neovascularization in late-onset retinal macular degeneration. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2019;3:153. - PubMed
-
- Kuntz CA, et al. Sub-retinal pigment epithelial deposits in a dominant late-onset retinal degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996;37:1772–1782. - PubMed

