PPIL4 is essential for brain angiogenesis and implicated in intracranial aneurysms in humans
- PMID: 34887573
- PMCID: PMC8768030
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01572-7
PPIL4 is essential for brain angiogenesis and implicated in intracranial aneurysms in humans
Abstract
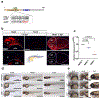
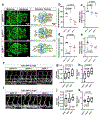
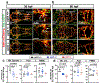
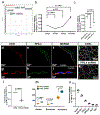
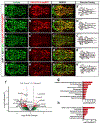
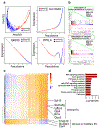
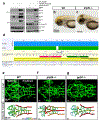
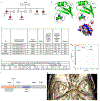
Intracranial aneurysm (IA) rupture leads to subarachnoid hemorrhage, a sudden-onset disease that often causes death or severe disability. Although genome-wide association studies have identified common genetic variants that increase IA risk moderately, the contribution of variants with large effect remains poorly defined. Using whole-exome sequencing, we identified significant enrichment of rare, deleterious mutations in PPIL4, encoding peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase-like 4, in both familial and index IA cases. Ppil4 depletion in vertebrate models causes intracerebral hemorrhage, defects in cerebrovascular morphology and impaired Wnt signaling. Wild-type, but not IA-mutant, PPIL4 potentiates Wnt signaling by binding JMJD6, a known angiogenesis regulator and Wnt activator. These findings identify a novel PPIL4-dependent Wnt signaling mechanism involved in brain-specific angiogenesis and maintenance of cerebrovascular integrity and implicate PPIL4 gene mutations in the pathogenesis of IA.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Vlak MH, Algra A, Brandenburg R & Rinkel GJ Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 10, 626–636 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Lindbohm JV, Kaprio J, Jousilahti P, Salomaa V & Korja M Risk factors of sudden death from subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 48, 2399–2404 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Kissela BM et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: a preventable disease with a heritable component. Stroke 33, 1321–1326 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

