Place-Based Drivers of Mortality: Evidence from Migration
- PMID: 34887592
- PMCID: PMC8653912
- DOI: 10.1257/aer.20190825
Place-Based Drivers of Mortality: Evidence from Migration
Abstract
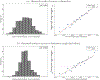
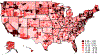
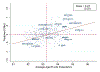
We estimate the effect of current location on elderly mortality by analyzing outcomes of movers in the Medicare population. We control for movers' origin locations as well as a rich vector of pre-move health measures. We also develop a novel strategy to adjust for remaining unobservables, using the correlation of residual mortality with movers' origins to gauge the importance of omitted variables. We estimate substantial effects of current location. Moving from a 10th to a 90th percentile location would increase life expectancy at age 65 by 1.1 years, and equalizing location effects would reduce cross-sectional variation in life expectancy by 15 percent. Places with favorable life expectancy effects tend to have higher quality and quantity of health care, less extreme climates, lower crime rates, and higher socioeconomic status.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Association of Geographic Differences in Prevalence of Uncontrolled Chronic Conditions With Changes in Individuals' Likelihood of Uncontrolled Chronic Conditions.JAMA. 2020 Oct 13;324(14):1429-1438. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.14381. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 33048153 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the 1990 Hong Kong legislation for restriction on sulfur content in fuel.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012 Aug;(170):5-91. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012. PMID: 23316618
-
Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories.Lancet. 2018 Nov 10;392(10159):2052-2090. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31694-5. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Lancet. 2018. PMID: 30340847 Free PMC article.
-
Difficult Life Events, Selective Migration and Spatial Inequalities in Mental Health in the UK.PLoS One. 2015 May 27;10(5):e0126567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126567. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26018595 Free PMC article.
-
Internal migration in Turkey: socioeconomic characteristics by destination and type of move, 1965-70.Stud Comp Int Dev. 1983 Winter;18(4):76-111. doi: 10.1007/BF02686501. Stud Comp Int Dev. 1983. PMID: 12313235
Cited by
-
Geographic disparities in Alzheimer's disease and related dementia mortality in the US: Comparing impacts of place of birth and place of residence.SSM Popul Health. 2024 Aug 20;27:101708. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2024.101708. eCollection 2024 Sep. SSM Popul Health. 2024. PMID: 39262769 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to urban and rural contexts shapes smartphone usage behavior.PNAS Nexus. 2023 Nov 28;2(11):pgad357. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad357. eCollection 2023 Nov. PNAS Nexus. 2023. PMID: 38034094 Free PMC article.
-
The Causal Effects of Place on Health and Longevity.J Econ Perspect. 2021 Fall;35(4):147-170. doi: 10.1257/jep.35.4.147. J Econ Perspect. 2021. PMID: 37736159 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is There a VA Advantage? Evidence from Dually Eligible Veterans.Am Econ Rev. 2023 Nov;113(11):3003-3043. doi: 10.1257/aer.20211638. Am Econ Rev. 2023. PMID: 39816722 Free PMC article.
-
Public and Private Options in Practice: The Military Health System.Am Econ J Econ Policy. 2023 Nov;15(4):37-74. doi: 10.1257/pol.20210625. Am Econ J Econ Policy. 2023. PMID: 38031535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaronson Daniel. 1998. “Using Sibling Data to Estimate the Impact of Neighborhoods on Children’s Educational Outcomes.” Journal of Human Resources, 33(4): 915–946.
-
- Abowd John M., Kramarz Francis, and Margolis David N.. 1999. “High Wage Workers and High Wage Firms.” Econometrica, 67(2): 251–333.
-
- Abowd John M., Creecy Robert H., and Kramarz Francis. 2002. “Computing Person and Firm Effects Using Linked Longitudinal Employer-Employee Data.” U.S. Census Bureau Center for Economic Studies Longitudinal Employer-Household Dynamics Technical Papers 2002–06.
-
- Allcott Hunt, Diamond Rebecca, Dubé Jean-Pierre, Handbury Jessie, Rahkovsky Ilya, and Schnell Molly. 2019. “Food deserts and the causes of nutritional inequality.” The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 134(4): 1793–1844.
-
- Allison David B., Fontaine Kevin R., Manson JoAnn E., Stevens June, and VanItallie Theodore B.. 1999. “Annual Deaths Attributable to Obesity in the United States.” Journal of the American Medical Association, 282(16): 1530–1538. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
