Oral Health and Patterns of Dental Visits Among Diabetic Patients in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 34887684
- PMCID: PMC8653708
- DOI: 10.2147/CCIDE.S340579
Oral Health and Patterns of Dental Visits Among Diabetic Patients in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Purpose: Diabetes is a big public health threat in Saudi Arabia. However, there is limited evidence about dental problems, oral hygiene practices, and dental visits among diabetic patients. The study aimed to evaluate self-perceived oral health status and patterns of dental attendance among diabetic patients in the Eastern province of Saudi Arabia.
Methodology: This cross-sectional study included 486 diabetic patients (mean age 50.14±13.59 years) registered with the Saudi Diabetes Society, Saudi Arabia (October-November 2020). The World Health Organization's oral health questionnaire for adults was administered to collect information about oral health status, oral hygiene practices, and dental attendance, in addition to sociodemographic data. Descriptive and analytical statistics were performed.
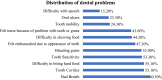
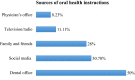
Results: Most participants (66.3%) reported having dental pain or discomfort during the last year. Bad breath (60.50%), tooth cavities (55.10%), difficulty in biting hard food (55.10%), tooth sensitivity (53.30%), and bleeding gums (52.90%) were common oral problems among participants. More than half the sample (55.1%) reported visiting the dental office during the last year. However, pain or trouble with teeth, gums or mouth was the most common (40.5%) reason for the last dental visit. Only 7.8% of participants visited the dentist for a routine dental check-up. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that Saudi nationality (AOR 2.68, P 0.008), family history of diabetes (AOR 1.88, P 0.022), and having pain during the last year (AOR 4.01, P <0.001) were the significant factors associated with the last dental visit due to pain.
Conclusion: This sample of participants demonstrated a high prevalence of dental problems. Few participants performed routine dental visits and most visits were due to pain. Saudis and patients with family history of diabetes and dental pain were more likely to perform pain related dental visits. Multidisciplinary efforts are needed to develop and implement preventive educational and clinical care models for positive oral and general health outcomes.
Keywords: access to oral care; dental problems; diabetes; oral health.
© 2021 AlTuraiki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dental Anxiety Among Physicians: Relationship with Oral Problems, Dental Visits, and Socio-Demographic Factors.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2023 Apr 20;17:1107-1116. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S406105. eCollection 2023. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2023. PMID: 37113214 Free PMC article.
-
Dental Visits and Predictors of Regular Attendance Among Female Schoolchildren in Dammam, Saudi Arabia.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2021 Mar 17;13:97-104. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S300108. eCollection 2021. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2021. PMID: 33762854 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Routine Dental Check-up Among Male Adolescents in Saudi Arabia.Acta Stomatol Croat. 2019 Sep;53(3):255-263. doi: 10.15644/asc53/3/7. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2019. PMID: 31749457 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of dental visits and their predictors among male adolescents.Dent Med Probl. 2018 Apr-Jun;55(2):185-190. doi: 10.17219/dmp/87023. Dent Med Probl. 2018. PMID: 30152623
-
The burden of Diabetes, Its Oral Complications and Their Prevention and Management.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Aug 15;6(8):1545-1553. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.294. eCollection 2018 Aug 20. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30159091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dental Anxiety Among Physicians: Relationship with Oral Problems, Dental Visits, and Socio-Demographic Factors.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2023 Apr 20;17:1107-1116. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S406105. eCollection 2023. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2023. PMID: 37113214 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of oral health-related quality of life and its association with mental health status of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the post-COVID-19 pandemic era: A study from Central Saudi Arabia.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 24;11:1158979. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1158979. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37033065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam U, Asghar O, Azmi S, Malik RA. General aspects of diabetes mellitus. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;126:211–222. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Diabetes. World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- Nagarajappa R, Sahare P, Shukla N, Tuteja J, Bhalla A. Knowledge, attitude and practices regarding oral health among out patients at Rama dental college, Kanpur. Rama Univ J Dent Sci. 2015;2(1):8–14.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials