Tanimilast, A Novel Inhaled Pde4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 34887752
- PMCID: PMC8650159
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.740803
Tanimilast, A Novel Inhaled Pde4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
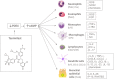
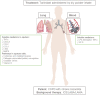
Chronic respiratory diseases are the third leading cause of death, behind cardiovascular diseases and cancer, affecting approximately 550 million of people all over the world. Most of the chronic respiratory diseases are attributable to asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with this latter being the major cause of deaths. Despite differences in etiology and symptoms, a common feature of asthma and COPD is an underlying degree of airways inflammation. The nature and severity of this inflammation might differ between and within different respiratory conditions and pharmacological anti-inflammatory treatments are unlikely to be effective in all patients. A precision medicine approach is needed to selectively target patients to increase the chance of therapeutic success. Inhibitors of the phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) enzyme like the oral PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast have shown a potential to reduce inflammatory-mediated processes and the frequency of exacerbations in certain groups of COPD patients with a chronic bronchitis phenotype. However, roflumilast use is dampened by class related side effects as nausea, diarrhea, weight loss and abdominal pain, resulting in both substantial treatment discontinuation in clinical practice and withdrawal from clinical trials. This has prompted the search for PDE4 inhibitors to be given by inhalation to reduce the systemic exposure (and thus optimize the systemic safety) and maximize the therapeutic effect in the lung. Tanimilast (international non-proprietary name of CHF6001) is a novel highly potent and selective inhaled PDE4 inhibitor with proven anti-inflammatory properties in various inflammatory cells, including leukocytes derived from asthma and COPD patients, as well as in experimental rodent models of pulmonary inflammation. Inhaled tanimilast has reached phase III clinical development by showing promising pharmacodynamic results associated with a good tolerability and safety profile, with no evidence of PDE4 inhibitors class-related side effects. In this review we will discuss the main outcomes of preclinical and clinical studies conducted during tanimilast development, with particular emphasis on the characterization of the pharmacodynamic profile that led to the identification of target populations with increased therapeutic potential in inflammatory respiratory diseases.
Keywords: COPD—chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; asthma; inflammation; inhaled administration; phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors (PDE4i).
Copyright © 2021 Facchinetti, Civelli, Singh, Papi, Emirova and Govoni.
Conflict of interest statement
FF, MC, AE, and MG were employed by Chiesi, the sponsor of all tanimilast studies. DS received personal fees from Chiesi during the conduct of this study. Outside the submitted work, he reports grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Glenmark, Menarini, Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Pulmatrix, Therevance, and Verona, and personal fees from Cipla, Genentech and Peptinnovate. AP reports grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi Farmaceutici GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi/Regeneron and TEVA, personal fees from Edmondpharma, Menarini, Mundipharma, Novartis, Roche and Zambon, grants from AIFA Ricerca Indipendente, Fondazione Maugeri, all outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor Therapy Be Used in Respiratory Diseases Other Than Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?Cureus. 2022 Jul 22;14(7):e27132. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27132. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36017299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhaled Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) Inhibitors for Inflammatory Respiratory Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 12;11:259. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00259. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32226383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast--a selective, oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Aug;23(4):235-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.03.011. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20381629 Review.
-
The PDE4 Inhibitor Tanimilast Blunts Proinflammatory Dendritic Cell Activation by SARS-CoV-2 ssRNAs.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 24;12:797390. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.797390. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35140709 Free PMC article.
-
The need for inhaled phosphodiesterase inhibitors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Dec;17(12):1149-1161. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2024.2438187. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39625645 Review.
Cited by
-
Burden of Exacerbations in Patients Newly Initiating an Inhaled Regimen for COPD: A Claims Analysis.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jun 7;20:1829-1842. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S517864. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40510054 Free PMC article.
-
The PDE4 Inhibitor Tanimilast Restrains the Tissue-Damaging Properties of Human Neutrophils.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 29;23(9):4982. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094982. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563373 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targets and Precision Medicine in COPD: Inflammation, Ion Channels, Both, or Neither?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 11;24(24):17363. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417363. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asthma and Post-Asthmatic Fibrosis: A Search for New Promising Molecular Markers of Transition from Acute Inflammation to Pulmonary Fibrosis.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 28;10(5):1017. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051017. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625754 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4B inhibition: a potential novel strategy for treating pulmonary fibrosis.Eur Respir Rev. 2023 Feb 21;32(167):220206. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0206-2022. Print 2023 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2023. PMID: 36813290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

