AbobotulinumtoxinA provides flexibility for the treatment of cervical dystonia with 500 U/1 mL and 500 U/2 mL dilutions
- PMID: 34888518
- PMCID: PMC8636802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2021.100115
AbobotulinumtoxinA provides flexibility for the treatment of cervical dystonia with 500 U/1 mL and 500 U/2 mL dilutions
Abstract
Introduction: Cervical dystonia (CD) is a neurologic movement disorder with potentially disabling effects and significant impact on quality of life of those affected. AbobotulinumtoxinA (aboBoNT-A) was initially approved for a dilution of 500 U/1 mL and subsequently for a dilution of 500 U/2 mL, providing flexibility for clinicians to treat CD. Here, we explore the safety and efficacy of the 500 U/2 mL dilution versus 500 U/1 mL dilution of aboBoNT-A in a retrospective analysis based on published clinical trial data.
Methods: The safety and efficacy of aboBoNT-A in patients with CD was evaluated in three multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials and open-label extensions. Trials 1 (NCT00257660) and 2 (NCT00288509) evaluated the 500 U/1 mL dilution in 80 and 116 patients, respectively; Trial 3 (NCT01753310) evaluated the 500 U/2 mL dilution in 125 patients.
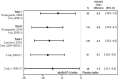
Results: Comparison of the adjusted mean difference in TWSTRS total scores at Week 4 from baseline for aboBoNT-A in Trial 1 (-6.0; 95% CI, -10.8, -1.3), Trial 2 (-8.8; 95% CI, -12.9, -4.7), and Trial 3 (-8.7; 95% CI, -13.2, -4.2) showed similar, significant improvements. Dysphagia and muscle weakness patterns were comparable across the three trials, indicating that an increased dilution of aboBoNT-A does not result in an increased risk of diffusion-related adverse events.
Conclusion: The results of these trials show that aboBoNT-A is similarly efficacious using either dilution, with similar safety and tolerability across trials. Having the 500 U/1 mL and 500 U/2 mL dilution volumes available provides further flexibility in administration, benefiting patient care.
Keywords: AbobotulinumtoxinA; Cervical dystonia; Dilution; Dosing flexibility; Treatment.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SHI received honoraria, consultancy, and promotional speaker fees from Ipsen. ATP received consultant and speaker fees from Ipsen. AB received consultancy fees from Ipsen. KD received advisor/consultant/speaker fees from Ipsen. LB received honoraria from Ipsen. SHI, DT, and ATP received research grants/support from Ipsen. PM is employed by Ipsen, and SW is a former employee of Ipsen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AbobotulinumtoxinA using 2-mL dilution (500 U/2-mL) maintains durable improvement across multiple treatment cycles.J Clin Mov Disord. 2020 Aug 31;7:8. doi: 10.1186/s40734-020-00090-x. eCollection 2020. J Clin Mov Disord. 2020. PMID: 32884828 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained functional benefits after a single set of injections with abobotulinumtoxinA using a 2-mL injection volume in adults with cervical dystonia: 12-week results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3b study.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 1;16(2):e0245827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245827. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33524060 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A 500 U/2 mL dilution of abobotulinumtoxinA vs. placebo: randomized study in cervical dystonia.Int J Neurosci. 2018 Jul;128(7):619-626. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2017.1406935. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Int J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29343142 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA versus onabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of refractory neurogenic detrusor overactivity: a systematic review and indirect treatment comparison.J Med Econ. 2023 Jan-Dec;26(1):200-207. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2023.2165366. J Med Econ. 2023. PMID: 36647624
-
Comparative efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness of abobotulinumtoxinA and onabotulinumtoxinA in children with upper limb spasticity: a systematic literature review, indirect treatment comparison, and economic evaluation.J Med Econ. 2021 Jan-Dec;24(1):949-961. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2021.1957582. J Med Econ. 2021. PMID: 34340647
References
-
- Albanese A., Abbruzzese G., Dressler D., Duzynski W., Khatkova S., Marti M.J., Mir P., Montecucco C., Moro E., Pinter M., Relja M., Roze E., Skogseid I.M., Timerbaeva S., Tzoulis C. Practical guidance for CD management involving treatment of botulinum toxin: a consensus statement. J. Neurol. 2015;262(10):2201–2213. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mordin M., Masaquel C., Abbott C., Copley-Merriman C. Factors affecting the health-related quality of life of patients with cervical dystonia and impact of treatment with abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport): results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. BMJ Open. 2014;4(10):e005150. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005150. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simpson D.M., Hallett M., Ashman E.J., Comella C.L., Green M.W., Gronseth G.S., Armstrong M.J., Gloss D., Potrebic S., Jankovic J., Karp B.P., Naumann M., So Y.T., Yablon S.A. Practice guideline update summary: botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2016;86(19):1818–1826. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Truong D., Duane D.D., Jankovic J., Singer C., Seeberger L.C., Comella C.L., Lew M.F., Rodnitzky R.L., Danisi F.O., Sutton J.P., Charles P.D., Hauser R.A., Sheean G.L. Efficacy and safety of botulinum type A toxin (Dysport) in cervical dystonia: results of the first US randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Mov. Disord. 2005;20(7):783–791. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

