Prebiotic to Improve Calcium Absorption in Postmenopausal Women After Gastric Bypass: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 34888663
- PMCID: PMC8947782
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab883
Prebiotic to Improve Calcium Absorption in Postmenopausal Women After Gastric Bypass: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Context: The adverse skeletal effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) are partly caused by intestinal calcium absorption decline. Prebiotics, such as soluble corn fiber (SCF), augment colonic calcium absorption in healthy individuals.
Objective: We tested the effects of SCF on fractional calcium absorption (FCA), biochemical parameters, and the fecal microbiome in a post-RYGB population.
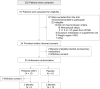
Methods: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 20 postmenopausal women with history of RYGB a mean 5 years prior; a 2-month course of 20 g/day SCF or maltodextrin placebo was taken orally. The main outcome measure was between-group difference in absolute change in FCA (primary outcome) and was measured with a gold standard dual stable isotope method. Other measures included tolerability, adherence, serum calciotropic hormones and bone turnover markers, and fecal microbial composition via 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
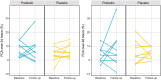
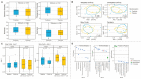
Results: Mean FCA ± SD at baseline was low at 5.5 ± 5.1%. Comparing SCF to placebo, there was no between-group difference in mean (95% CI) change in FCA (+3.4 [-6.7, +13.6]%), nor in calciotropic hormones or bone turnover markers. The SCF group had a wider variation in FCA change than placebo (SD 13.4% vs 7.0%). Those with greater change in microbial composition following SCF treatment had greater increase in FCA (r2 = 0.72, P = 0.05). SCF adherence was high, and gastrointestinal symptoms were similar between groups.
Conclusion: No between-group differences were observed in changes in FCA or calciotropic hormones, but wide CIs suggest a variable impact of SCF that may be due to the degree of gut microbiome alteration. Daily SCF consumption was well tolerated. Larger and longer-term studies are warranted.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03272542.
Keywords: bariatric surgery; calcium absorption; gastric bypass; obesity; prebiotic.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society 2021.
Figures
References
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020;(360):1-8. - PubMed
-
- Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. . Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292(14):1724-1737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

