Astrocytes: The Housekeepers and Guardians of the CNS
- PMID: 34888829
- PMCID: PMC9004589
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-77375-5_2
Astrocytes: The Housekeepers and Guardians of the CNS
Abstract
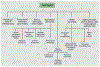
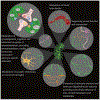
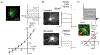
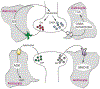
Astroglia are a diverse group of cells in the central nervous system. They are of the ectodermal, neuroepithelial origin and vary in morphology and function, yet, they can be collectively defined as cells having principle function to maintain homeostasis of the central nervous system at all levels of organisation, including homeostasis of ions, pH and neurotransmitters; supplying neurones with metabolic substrates; supporting oligodendrocytes and axons; regulating synaptogenesis, neurogenesis, and formation and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier; contributing to operation of the glymphatic system; and regulation of systemic homeostasis being central chemosensors for oxygen, CO2 and Na+. Their basic physiological features show a lack of electrical excitability (inapt to produce action potentials), but display instead a rather active excitability based on variations in cytosolic concentrations of Ca2+ and Na+. It is expression of neurotransmitter receptors, pumps and transporters at their plasmalemma, along with transports on the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria that exquisitely regulate the cytosolic levels of these ions, the fluctuation of which underlies most, if not all, astroglial homeostatic functions.
Keywords: Astroglia; Brain homoeostasis; Ca2+ signalling; Ion channels; Na+ signalling; Neurotransmitter receptors; SLC transporters.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Figures

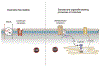


References
-
- Allen A, Messier C (2013) Plastic changes in the astrocyte GLUT1 glucose transporter and beta-tubulin microtubule protein following voluntary exercise in mice. Behav Brain Res 240:95–102 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez J, Montero M (2002) Measuring [Ca2+] in the endoplasmic reticulum with aequorin. Cell Calcium 32:251–260 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
