Multiseptate gallbladder: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 34889244
- PMCID: PMC8663827
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027992
Multiseptate gallbladder: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Multiseptate gallbladder (MSG) is a rare congenital gallbladder anomaly. Between 1963 and June 2021, only 56 cases were reported. There is currently no treatment guideline for pediatric or adult cases of MSG.
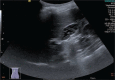
Patient concerns: A 14-year-old woman visited our out-patient clinic in September 2020 for epigastric pain that last for 6 months. Honeycomb appearance of the gallbladder was noted under ultrasonography.
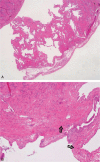
Diagnosis: The patient was diagnosed with MSG. The diagnosis was confirmed through computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
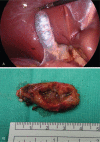
Interventions: Cholecystectomy was performed.
Outcomes: Epigastric pain showed limited improvement after the surgery. Since she was diagnosed with gastritis at the same time, a proton-pump inhibitor was prescribed. Epigastric pain was eventually resolved.
Lessons: MSG cases can undergo cholecystectomy and show good recovery without complications. However, concomitant treatment may be required to resolve in the presence of other symptoms such as epigastric pain.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Simon M, Tandon BN. Multiseptate gallbladder. A case report. Radiology 1963;80:84–6. - PubMed
-
- Haslam RH, Gayler BW, Ebert PA. Multiseptate gallbladder. A cause of recurrent abdominal pain in childhood. Am J Dis Child 1966;112:600–3. - PubMed
-
- Singh AD, Simons-Linares CR, Chahal P. A dilated common bile duct with “atypical” gallbladder. Gastroenterology 2020;159:e6–7. - PubMed
-
- Esper E, Kaufman DB, Crary GS, Snover DC, Leonard AS. Septate gallbladder with cholelithiasis: a cause of chronic abdominal pain in a 6-year-old child. J Pediatr Surg 1992;27:1560–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

