Loneliness, Risky Beliefs and Intentions about Practicing Safer Sex among Methamphetamine Dependent Individuals
- PMID: 34889707
- PMCID: PMC8922988
- DOI: 10.1080/10826084.2021.2003404
Loneliness, Risky Beliefs and Intentions about Practicing Safer Sex among Methamphetamine Dependent Individuals
Abstract
Background: Methamphetamine use is a known predictor of riskier sexual behaviors, which can have important public health implications (e.g., HIV-transmission risk). Loneliness also is associated with riskier sexual behaviors, though the relationship between loneliness and beliefs and/or intentions to practice safer sex has not been examined among people dependent on methamphetamine.
Materials and methods: Individuals who met DSM-IV criteria for lifetime methamphetamine dependence and current (≤ 18-months) methamphetamine abuse or dependence (METH+ n = 56) were compared to those without severity and recency of methamphetamine use (METH- n = 59). These groups did not differ on social network size or proportion of people with HIV (∼58% HIV+). Participants completed the NIH Toolbox Loneliness Scale and the Sexual Risks Scale's "Norms" and "Intentions" subscales.
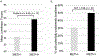
Results: METH+ individuals were significantly lonelier than METH- controls (t(113) = 2.45, p = .02). Methamphetamine dependence remained significantly associated with greater loneliness, after controlling for HIV status and other relevant covariates (e.g., neurocognitive impairment, history of mood disorder, social network size; F = 3.70, Adjusted R2 = 0.18, p = .0009). Loneliness, above and beyond the aforementioned covariates, was significantly associated with riskier beliefs and intentions to practice safer sex among METH+, but not METH-, individuals (β = 2.92, p = .02).
Conclusions: Loneliness is prevalent among individuals dependent on methamphetamine, and is uniquely associated with riskier beliefs and intentions regarding practicing safer sex. Findings may aid in identifying individuals at-risk of engaging in riskier sexual behaviors and guide risk prevention strategies.
Keywords: HIV; Loneliness; methamphetamine dependence; norms; risky sexual behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the article
Figures


References
-
- Abell JG, Abell J, Cadar D, Llewellyn DJ, & Steptoe A (2019). Loneliness, social isolation, and domains of cognitive impairment in the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Innovation in Aging, 3(Suppl_1), S190–S191. 10.1093/geroni/igz038.684 - DOI
-
- APA. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.
-
- Babakhanyan I, McKenna BS, Casaletto KB, Nowinski CJ, & Heaton RK (2018). National institutes of health toolbox emotion battery for English- and Spanish-speaking adults: Normative data and factor-based summary scores. Patient Related Outcome Measures, 9, 115–127. 10.2147/PROM.S151658 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
