Transporting an Artificial Intelligence Model to Predict Emergency Cesarean Delivery: Overcoming Challenges Posed by Interfacility Variation
- PMID: 34890352
- PMCID: PMC8709908
- DOI: 10.2196/28120
Transporting an Artificial Intelligence Model to Predict Emergency Cesarean Delivery: Overcoming Challenges Posed by Interfacility Variation
Abstract
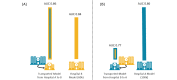
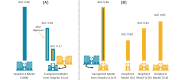
Research using artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine is expected to significantly influence the practice of medicine and the delivery of health care in the near future. However, for successful deployment, the results must be transported across health care facilities. We present a cross-facilities application of an AI model that predicts the need for an emergency caesarean during birth. The transported model showed benefit; however, there can be challenges associated with interfacility variation in reporting practices.
Keywords: AI; ML; algorithm transport; artificial intelligence; birth; health care facilities; health outcomes; machine learning; neonatal; pediatrics; pregnancy; prenatal.
©Joshua Guedalia, Michal Lipschuetz, Sarah M Cohen, Yishai Sompolinsky, Asnat Walfisch, Eyal Sheiner, Ruslan Sergienko, Joshua Rosenbloom, Ron Unger, Simcha Yagel, Hila Hochler. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 10.12.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Miotto R, Wang F, Wang S, Jiang X, Dudley JT. Deep learning for healthcare: review, opportunities and challenges. Brief Bioinform. 2018 Nov 27;19(6):1236–1246. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx044. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28481991 3800524 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kelly CJ, Karthikesalingam A, Suleyman M, Corrado G, King D. Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence. BMC Med. 2019 Oct 29;17(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12916-019-1426-2. https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-019-1426-2 10.1186/s12916-019-1426-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

