Tartary buckwheat flavonoids relieve the tendency of mammary fibrosis induced by HFD during pregnancy and lactation
- PMID: 34890369
- PMCID: PMC8714130
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203752
Tartary buckwheat flavonoids relieve the tendency of mammary fibrosis induced by HFD during pregnancy and lactation
Abstract
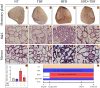
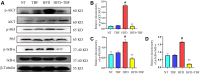
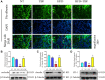
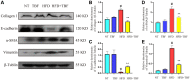
Mammary gland fibrosis is a chronic and irreversible disease. Tartary buckwheat flavonoids (TBF) are a natural product of flavonoid extracts from buckwheat and have a wide range of biological activities. The purpose of this experiment was to explore whether HFD during pregnancy and lactation induces fibrosis of the mammary tissue and whether TBF alleviates the damage caused by HFD, along with its underlying mechanism. The HFD significantly increased the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and MPO; significantly damaged the integrity of the blood-milk barrier; significantly increased the levels of collagen 1, vimentin and α-SMA, and reduced the level of E-cadherin. However, these effects were alleviated by TBF. Mechanistic studies showed that TBF inhibited the activation of AKT/NF-κB signaling and predicted the AKT amino acid residues that formed hydrogen bonds with TBF; in addition, these studies not only revealed that TBF promoted the expression of the tight junction proteins (TJs) claudin-3, occludin and ZO-1 and inhibited the activation of TGF-β/Smad signaling but also predicted the Smad MH2 amino acid residues that formed hydrogen bonds with TBF. Conclusion: HFD consumption during pregnancy and lactation induced the tendency of mammary fibrosis. TBF alleviated the tendency of mammary fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of AKT/NF-κB, repairing the blood-milk barrier and inhibiting the activation of TGF-β/Smad signaling.
Keywords: AKT/NF-κB; blood-milk barrier; fibrosis; high-fat diet; inflammatory microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tartary buckwheat flavonoids alleviates high-fat diet induced kidney fibrosis in mice by inhibiting MAPK and TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Jul 1;379:110533. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110533. Epub 2023 May 5. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 37150497
-
Morin alleviates LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT, MAPK, NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathway and protecting the integrity of blood-milk barrier.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jan;78:105972. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105972. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31711938
-
Tartary buckwheat flavonoids protect hepatic cells against high glucose-induced oxidative stress and insulin resistance via MAPK signaling pathways.Food Funct. 2016 Mar;7(3):1523-36. doi: 10.1039/c5fo01467k. Food Funct. 2016. PMID: 26899161
-
Tartary buckwheat flavonoids ameliorate high fructose-induced insulin resistance and oxidative stress associated with the insulin signaling and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways in mice.Food Funct. 2017 Aug 1;8(8):2803-2816. doi: 10.1039/c7fo00359e. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Food Funct. 2017. PMID: 28714504
-
Bioactive compounds, health benefits, and industrial applications of Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum).Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(5):657-673. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1952161. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 34278850 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Rutin and Other Phenolic Substances on the Digestibility of Buckwheat Grain Metabolites.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 1;23(7):3923. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073923. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sanguinarine Enhances the Integrity of the Blood-Milk Barrier and Inhibits Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Mastitis.Cells. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3658. doi: 10.3390/cells11223658. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429086 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

