Patho-mechanisms of the origins of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- PMID: 34894313
- PMCID: PMC8665964
- DOI: 10.1186/s40348-021-00129-5
Patho-mechanisms of the origins of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Abstract
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) continues to be one of the most common complications of prematurity, despite significant advancement in neonatology over the last couple of decades. The new BPD is characterized histopathologically by impaired lung alveolarization and dysregulated vascularization. With the increased survival of extremely preterm infants, the risk for the development of BPD remains high, emphasizing the continued need to understand the patho-mechanisms that play a role in the development of this disease. This brief review summarizes recent advances in our understanding of the maldevelopment of the premature lung, highlighting recent research in pathways of oxidative stress-related lung injury, the role of placental insufficiency, growth factor signaling, the extracellular matrix, and microRNAs.
Keywords: Chronic lung disease; Growth factors; Hyperoxia; Placenta; Preterm lung; miRNA.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
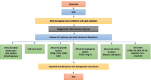
References
-
- Northway WH, Jr, Rosan RC, Porter DY. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967;276(7):357–368. - PubMed
-
- Husain AN, Siddiqui NH, Stocker JT. Pathology of arrested acinar development in postsurfactant bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Hum Pathol. 1998;29(7):710–717. - PubMed
-
- De Paepe ME. Pathology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. In: Bhandari V, editor. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2016. pp. 149–164.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

