Effectiveness of social distancing interventions in containing COVID-19 incidence: International evidence using Kalman filter
- PMID: 34894622
- PMCID: PMC8638209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ehb.2021.101091
Effectiveness of social distancing interventions in containing COVID-19 incidence: International evidence using Kalman filter
Abstract
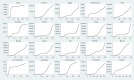
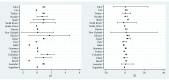
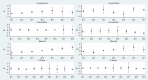
The epidemiological literature has widely documented the importance of social distancing interventions in containing the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the epidemiological measure of virus reproduction, R0, provides a myopic view of containment, especially when the absolute number of cases is still high. The paper investigates cross-country variations concerning the impact of social distancing interventions on COVID-19 incidence by employing a statistical measure of containment, which models the daily number of cases as a structural time-series, state-space vector. Countries that adopt strict lockdown policies and provide economic support in the form of income augmentations and debt relief improve the response towards the pandemic. Countries like China and South Korea have been most influential in containing the spread of infections. European nations of France, Italy, Spain and the UK are witnessing a second wave of the virus, indicating that re-opening the European economy perhaps has instigated an exponential spread.
Keywords: COVID-19; Economic epidemiology; Kalman filter; Non-pharmaceutical interventions; Pandemic; Social distancing.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures






References
-
- Anderson B., Moore J. Prentice Hall; Englewood Cliffs: 1979. Optimal Filtering.
-
- Arellano M., Bond S. Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1991;51:277–297.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

