TNP and its analogs: Modulation of IP6K and CYP3A4 inhibition
- PMID: 34894957
- PMCID: PMC8667942
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2021.2000404
TNP and its analogs: Modulation of IP6K and CYP3A4 inhibition
Abstract
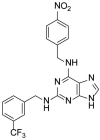
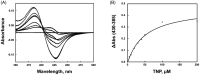
Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase (IP6K) is an important mammalian enzyme involved in various biological processes such as insulin signalling and blood clotting. Recent analyses on drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic properties on TNP (N2-(m-trifluorobenzyl), N6-(p-nitrobenzyl)purine), a pan-IP6K inhibitor, have suggested that it may inhibit cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes and induce unwanted drug-drug interactions in the liver. In this study, we confirmed that TNP inhibits CYP3A4 in type I binding mode more selectively than the other CYP450 isoforms. In an effort to find novel purine-based IP6K inhibitors with minimal CYP3A4 inhibition, we designed and synthesised 15 TNP analogs. Structure-activity relationship and biochemical studies, including ADP-Glo kinase assay and quantification of cell-based IP7 production, showed that compound 9 dramatically reduced CYP3A4 inhibition while retaining IP6K-inhibitory activity. Compound 9 can be a tool molecule for structural optimisation of purine-based IP6K inhibitors.
Keywords: Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase; cytochrome P450 3A4; structure-activity relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures




References
-
- Irvine RF, Schell MJ.. Back in the water: the return of the inositol phosphates. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001;2:327–38. - PubMed
-
- Park SJ, Lee S, Park SE, Kim S.. Inositol pyrophosphates as multifaceted metabolites in the regulation of mammalian signaling networks. Animal Cells and Systems 2018;22:1–6.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
