Discovery of a novel Aurora B inhibitor GSK650394 with potent anticancer and anti- aspergillus fumigatus dual efficacies in vitro
- PMID: 34894976
- PMCID: PMC8667888
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1975693
Discovery of a novel Aurora B inhibitor GSK650394 with potent anticancer and anti- aspergillus fumigatus dual efficacies in vitro
Abstract
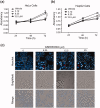
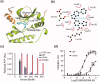
Invasive fungal infections including Candidiasis and Aspergillosis are associated with considerable morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised individuals, such as cancer patients. Aurora B is a key mitotic kinase required for the cell division of eukaryotes from fungus to man. Here, we identified a novel Aurora B inhibitor GSK650394 that can inhibit the recombinant Aurora B from human and Aspergillus fumigatus, with IC50 values of 5.68 and 1.29 µM, respectively. In HeLa and HepG2 cells, GSK650394 diminishes the endogenous Aurora B activity and causes cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase. Further cell-based assays demonstrate that GSK650394 efficiently suppresses the proliferation of both cancer cells and Aspergillus fumigatus. Finally, the molecular docking calculation and site-directed mutagenesis analyses reveal the molecular mechanism of Aurora B inhibition by GSK650394. Our work is expected to provide new insight into the combinational therapy of cancer and Aspergillus fumigatus infection.
Keywords: Aurora B; anti-aspergillus fumigatus; anti-cancer; inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Pagano L, Caira M, Candoni A, et al. The epidemiology of fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies: the SEIFEM-2004 study. Haematologica 2006;91:1068–75. - PubMed
-
- Steinmann J, Hamprecht A, Vehreschild MJ, et al. Emergence of azole-resistant invasive aspergillosis in HSCT recipients in Germany. J Antimicrob Chemother 2015;70:1522–6. - PubMed
-
- Kitzen JJ, de Jonge MJ, Verweij J.. Aurora kinase inhibitors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2010;73:99–110. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
