SARS-CoV-2-antibody response in health care workers after vaccination or natural infection in a longitudinal observational study
- PMID: 34895938
- PMCID: PMC8639476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.11.081
SARS-CoV-2-antibody response in health care workers after vaccination or natural infection in a longitudinal observational study
Abstract
Background: Following a year of development, several vaccines have been approved to contain the global COVID-19 pandemic. Real world comparative data on immune response following vaccination or natural infection are rare.
Methods: We conducted a longitudinal observational study in employees at a secondary care hospital affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. Comparisons were made about the presence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunglobulin G (IgG) antibody ratio after natural infection, or vaccination with one or two doses of BioNTech/Pfizer (BNT162b2), or one dose of AstraZenca (Vaxzevria) vaccine.
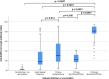
Results: We found a 100% humoral response rate in participants after 2 doses of BNT162b2 vaccine. The antibody ratio in participants with one dose BNT162b2 and Vaxzevria did not differ significantly to those with previous PCR-confirmed infection, whereas this was significantly lower in comparison to two doses of BioNTech/Pfizer. We could not identify a correlation with previous comorbidities, obesity or age within this study. Smoking showed a negative effect on the antibody response (p = 0.006) CONCLUSION: Our data provide an overview about humoral immune response after natural SARS-CoV-2 infection or following vaccination, and supports the usage of booster vaccinations, especially in patients after a natural SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: Anti-SARS-CoV-2-IgG-antibodies; AstraZeneca; BioNTech; Health Care worker; Seroprevalence; Vaccination.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard n.d. https://covid19.who.int (accessed August 31, 2020).
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S.A.C., Madhi S.A., Weckx L.Y., Folegatti P.M., Aley P.K., et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet (London, England) 2021;397:99–111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

