The Water-Soluble Chitosan Derivative, N-Methylene Phosphonic Chitosan, Is an Effective Fungicide against the Phytopathogen Fusarium eumartii
- PMID: 34897246
- PMCID: PMC8666248
- DOI: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.06.2021.0090
The Water-Soluble Chitosan Derivative, N-Methylene Phosphonic Chitosan, Is an Effective Fungicide against the Phytopathogen Fusarium eumartii
Abstract
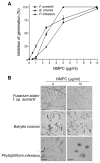
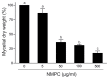
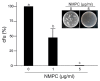
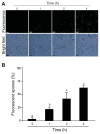
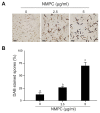
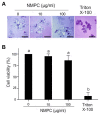
Chitosan has been considered an environmental-friendly polymer. However, its use in agriculture has not been extended yet due to its relatively low solubility in water. N-Methylene phosphonic chitosan (NMPC) is a water-soluble derivative prepared by adding a phosphonic group to chitosan. This study demonstrates that NMPC has a fungicidal effect on the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium solani f. sp. eumartii (F. eumartii) judged by the inhibition of F. eumartti mycelial growth and spore germination. NMPC affected fungal membrane permeability, reactive oxygen species production, and cell death. Also, this chitosan-derivative exerted antifungal effects against two other phytopathogens, Botrytis cinerea, and Phytophthora infestans. NMPC did not affect tomato cell viability at the same doses applied to these phytopathogens to exert fungicide action. In addition to water solubility, the selective biological cytotoxicity of NMPC adds value in its application as an antimicrobial agent in agriculture.
Keywords: Fusarium solani f. sp. eumartii; N-methylene phosphonic chitosan derivative; Solanum lycopersicum; antifungal activity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Andreu AB, Caldiz DO, Forbes GA. Phenotypic expression of resistance to Phytophthora infestans in processing potatoes in Argentina. Am J Potato Res. 2010;87:177–187.
-
- Asgari-Targhi G, Iranbakhsh A, Ardebili ZO. Potential benefits and phytotoxicity of bulk and nano-chitosan on the growth, morphogenesis, physiology, and micropropagation of Capsicum annuum . Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018;127:393–402. - PubMed
-
- Badawy MEI. Structure and antimicrobial activity relationship of quaternary N-alkyl chitosan derivatives against some plant pathogens. J Appl Polym Sci. 2010;117:960–969.
-
- Bautista-Baños S, Hernández-Lauzardo AN, Velázquez-del Valle MG, Hernández-López M, Ait Barka E, Bosquez-Molina E, Wilson CL. Chitosan as a potential natural compound to control pre and postharvest diseases of horticultural commodities. Crop Prot. 2006;25:108–118.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

