Characteristics of patients with axial spondyloarthritis by geographic regions: PROOF multicountry observational study baseline results
- PMID: 34897381
- PMCID: PMC9348765
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab901
Characteristics of patients with axial spondyloarthritis by geographic regions: PROOF multicountry observational study baseline results
Abstract
Objectives: To compare demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with axial SpA (axSpA) across geographic regions.
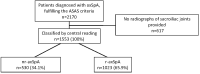
Methods: Patients With Axial Spondyloarthritis: Multicountry Registry of Clinical Characteristics (PROOF) is an observational study that enrolled recently diagnosed (≤1 year) axSpA patients fulfilling the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria from rheumatology clinical practices in 29 countries across six geographic regions. Demographics and disease-related parameters were collected. Here we present baseline data for patients who were classified as radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA) or non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA) confirmed by central reading.
Results: Of the 2170 patients enrolled, 1553 were classified based on central evaluation of sacroiliac radiographs [r-axSpA: 1023 (66%); nr-axSpA: 530 (34%)]. Patients with nr-axSpA had a significantly higher occurrence of enthesitis (40% vs 33%), psoriasis (10% vs 5%) and IBD (4% vs 2%) vs r-axSpA patients. Significant differences in axSpA characteristics were observed between geographic regions. The highest occurrence of peripheral arthritis (60%), enthesitis (52%) and dactylitis (12%) was in Latin America, and the lowest was in Canada (9%, 9% and 2%, respectively). The occurrence of uveitis and psoriasis was highest in Canada (18% and 14%, respectively) and lowest in China (6% and <1%, respectively). IBD was highest in Arabia (21%), and no cases were observed in China. In multivariable analysis adjusted for factors potentially affecting peripheral and extramusculoskeletal manifestations, geographic regions still exhibited significant differences in frequencies of uveitis (P < 0.01), psoriasis (P < 0.0001) and peripheral arthritis (P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: The multinational PROOF study of axSpA patients showed significant regional differences in peripheral and extramusculoskeletal manifestations of SpA, which could be considered in management guidelines and clinical trials.
Keywords: axial spondyloarthritis; characteristics; demographics; non-radiographic; radiographic.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Braun J, Sieper J.. Classification, diagnosis, and referral of patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2012;38:477–85. - PubMed
-
- Sieper J, Poddubnyy D.. Axial spondyloarthritis. Lancet 2017;390:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Feldtkeller E, Khan MA, van der Heijde D, van der Linden S, Braun J.. Age at disease onset and diagnosis delay in HLA-B27 negative vs. positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 2003;23:61–6. - PubMed
-
- Sykes MP, Doll H, Sengupta R, Gaffney K.. Delay to diagnosis in axial spondyloarthritis: are we improving in the UK? Rheumatology (Oxford) 2015;54:2283–4. - PubMed
-
- Redeker I, Callhoff J, Hoffmann F. et al. Determinants of diagnostic delay in axial spondyloarthritis: an analysis based on linked claims and patient-reported survey data. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2019;58:1634–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical