Advances in live imaging early mouse development: exploring the researcher's interdisciplinary toolkit
- PMID: 34897401
- PMCID: PMC7615354
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.199433
Advances in live imaging early mouse development: exploring the researcher's interdisciplinary toolkit
Abstract
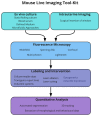
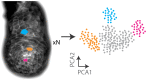
Live imaging is an important part of the developmental biologist's armoury of methods. In the case of the mouse embryo, recent advances in several disciplines including embryo culture, microscopy hardware and computational analysis have all contributed to our ability to probe dynamic events during early development. Together, these advances have provided us with a versatile and powerful 'toolkit', enabling us not only to image events during mouse embryogenesis, but also to intervene with them. In this short Spotlight article, we summarise advances and challenges in using live imaging specifically for understanding early mouse embryogenesis.
Keywords: Image analysis; Imaging developmental processes; Microscopy; Mouse embryology.
© 2021. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abe T, et al. Visualization of cell cycle in mouse embryos with Fucci2 reporter directed by Rosa26 promoter. Development. 2013;140(1):237–46. - PubMed
-
- Aguilera-Castrejon A, et al. Ex utero mouse embryogenesis from pre-gastrulation to late organogenesis. Nature. 2021;593(7857):119–24. - PubMed
-
- Beddington R. In: Mammalian Development: A Practical Approach. Monk M, editor. IRL Press Limited; Oxford: 1987. Isolation, culture, and manipulation of post-implantation mouse embryos; pp. 43–69.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

