YY1 and eIF4A3 are mediators of the cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma promoted by circ-ZNF609 by targeting miR-432-5p to regulate LRRC1
- PMID: 34898474
- PMCID: PMC8714144
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203735
YY1 and eIF4A3 are mediators of the cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma promoted by circ-ZNF609 by targeting miR-432-5p to regulate LRRC1
Abstract
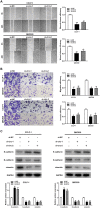
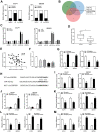
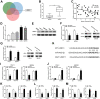
Cholangiocarcinoma is a highly aggressive malignant tumor, and its incidence is increasing all over the world. More and more evidences show that the aberrant expression of circular RNAs play important roles in tumorigenesis and progression. Current studies on the expression and function of circRNAs in cholangiocarcinoma are scarce. In this study, circ-ZNF609 was discovered as a novel circRNA highly expressed in cholangiocarcinoma for the first time. The circ-ZNF609 expression is connected with the advanced TNM stage, lymphatic invasion and survival time in cholangiocarcinoma patients, and can be used as an independent prognostic factor for the patients. Circ-ZNF609 can promote the cholangiocarcinoma cells proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro, it can also catalyze the xenograft growth in vivo. The promoting effect of circ-ZNF609 on cholangiocarcinoma is achieved via oncogene LRRC1 up-regulation through targeting miR-432-5p by endogenous competitive RNA mechanism. In addition, transcription factor YY1 can bind to the promoter of ZNF609 to further facilitate the transcription of circ-ZNF609. RNA binding protein eIF4A3 can bind to the pre-mRNA of circ-ZNF609 which promotes the circ-ZNF609 circular formation. Overall, YY1/eIF4A3/circ-ZNF609/miR-432-5p/LRRC1 have a significant role in progression of cholangiocarcinoma, and circ-ZNF609 is expected to become a novel biomarker for targeted therapy and prognosis evaluation of cholangiocarcinoma.
Keywords: LRRC1; YY1/eIF4A3; cholangiocarcinoma; circ-ZNF609; miR-432-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Tovoli F, Guerra P, Iavarone M, Veronese L, Renzulli M, De Lorenzo S, Benevento F, Brandi G, Stefanini F, Piscaglia F. Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Also Improves Survival of Incidentally Detected Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Arisen in Liver Cirrhosis. Liver Cancer. 2020; 9:744–55. 10.1159/000509059 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

