Low-Grade Primary Splenic CD10-Positive Small B-Cell Lymphoma/Follicular Lymphoma
- PMID: 34898578
- PMCID: PMC8628768
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol28060407
Low-Grade Primary Splenic CD10-Positive Small B-Cell Lymphoma/Follicular Lymphoma
Abstract
Primary splenic lymphoma (PSL) is a rare malignancy representing about 1% of all lymphoproliferative disorders, when using a strict definition that allows only involvement of spleen and hilar lymph nodes. In contrast, secondary low-grade B-cell lymphomas in the spleen, such as follicular lymphomas (FL), lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/ small lymphocytic lymphoma, particularly as part of advanced stage disease, are more common. Indolent B cell lymphomas expressing CD10 almost always represent FL, which in its primary splenic form is the focus of this review. Primary splenic follicular lymphoma (PSFL) is exceedingly infrequent. This type of lymphoproliferative disorder is understudied and, in most cases, clinically characterized by splenomegaly or cytopenias related to hypersplenism. The diagnosis requires correlation of histopathology of spleen, blood and/or bone marrow with the correct immunophenotype (determined by flow cytometry and/or immunohistochemistry) and if necessary, additional molecular profiling. Management of this incurable disease is evolving, and splenectomy remains the mainstream treatment for stage I PSFL.
Keywords: follicular lymphoma; low-grade B-cell lymphomas; primary splenic follicular lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
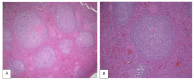

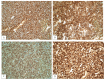
References
-
- Williamson J.M.S., Grigor I., Smith M.E.F., Holgate C.S., Quirke P., Bird C.C., Alison D.L., Child J.A. Cluster differentiation antigen expression, proliferative activity and clinical stage in centroblastic centrocytic lymphomas. J. Pathol. 1986;150:51–59. doi: 10.1002/path.1711500109. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choi W.W.L., Weisenburger D.D., Greiner T.C., Piris M.A., Banham A.H., Delabie J., Braziel R.M., Geng H., Iqbal J., Lenz G., et al. A new immunostain algorithm classifies diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into molecular subtypes with high accuracy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009;15:5494–5502. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

