The Up-regulation of TNF-α Maintains Trigeminal Neuralgia by Modulating MAPKs Phosphorylation and BKCa Channels in Trigeminal Nucleus Caudalis
- PMID: 34899191
- PMCID: PMC8657151
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.764141
The Up-regulation of TNF-α Maintains Trigeminal Neuralgia by Modulating MAPKs Phosphorylation and BKCa Channels in Trigeminal Nucleus Caudalis
Abstract
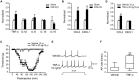
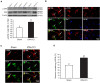
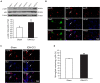
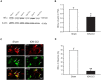
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a severe chronic neuropathic pain. Despite numerous available medical interventions, the therapeutic effects are not ideal. To control the pain attacks, the need for more contemporary drugs continues to be a real challenge. Our previous study reported that Ca2+-activated K+ channels (BK Ca ) channels modulated by mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in the trigeminal ganglia (TG) neurons play crucial roles in regulating TN, and some research studies demonstrated that inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) could promote neuropathic pain. Meanwhile, the trigeminal nucleus caudalis (TNC), the first central site of the trigeminal nociceptive pathway, is responsible for processing sensory and pain signals from the peripheral orofacial area. Thus, this study is aimed to further investigate whether TNF-α and MAPKs phosphorylation in the TNC could mediate the pathogenesis of TN by modulating BK Ca channels. The results showed that TNF-α of the TNC region is upregulated significantly in the chronic constriction injury of infraorbital nerve (ION-CCI) rats model, which displayed persistent facial mechanical allodynia. The normal rats with target injection of exogenous TNF-α to the fourth brain ventricle behaved just like the ION-CCI model rats, the orofacial mechanical pain threshold decreased clearly. Meanwhile, the exogenous TNF-α increased the action potential frequency and reduced the BK Ca currents of TNC neurons significantly, which could be reversed by U0126 and SB203580, the inhibitors of MAPK. In addition, U0126, SB203580, and another MAPK inhibitor SP600125 could relieve the facial mechanical allodynia by being injected into the fourth brain ventricle of ION-CCI model rats, respectively. Taken together, our work suggests that the upregulation of TNF-α in the TNC region would cause the increase of MAPKs phosphorylation and then the negative regulation of BK Ca channels, resulting in the TN.
Keywords: BKCa channel; MAPKs phosphorylation; TNF-α; trigeminal neuralgia; trigeminal nucleus caudalis.
Copyright © 2021 Lu, Fan, Yu, Ma and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The role of large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels in a rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain.Cephalalgia. 2015 Jan;35(1):16-35. doi: 10.1177/0333102414534083. Epub 2014 May 12. Cephalalgia. 2015. PMID: 24820887
-
[BK(Ca) channel agonist NS1619 and Kv channel antagonist 4-AP on the facial mechanical pain threshold in a rat model of chronic constriction injury of the infraorbital nerve].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2010 Oct 25;62(5):441-9. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 20945047 Chinese.
-
Involvement of the BNP/NPR-A/BKCa pathway in rat trigeminal ganglia following chronic constriction injury.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Apr 1;125(4):1139-1145. doi: 10.1152/jn.00682.2020. Epub 2021 Feb 17. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33596737
-
P2X3 receptor upregulation in trigeminal ganglion neurons through TNFα production in macrophages contributes to trigeminal neuropathic pain in rats.J Headache Pain. 2021 Apr 26;22(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01244-4. J Headache Pain. 2021. PMID: 33902429 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets for Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain.Medicines (Basel). 2019 Aug 22;6(3):91. doi: 10.3390/medicines6030091. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31443547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Olfactory Ensheathing Cells Alleviate Facial Pain in Rats with Trigeminal Neuralgia by Inhibiting the Expression of P2X7 Receptor.Brain Sci. 2022 May 30;12(6):706. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12060706. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35741592 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of 7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin in Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Trigeminal Neuralgia in a Rat Model.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 4;47(7):518. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070518. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728987 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Glucose Water as a Neural Injection: A Perspective on Neuroinflammation.Life (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;12(6):832. doi: 10.3390/life12060832. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35743863 Free PMC article.
-
GFAP-NpHR mediated optogenetic inhibition of trigeminal nucleus caudalis attenuates hypersensitive behaviors and thalamic discharge attributed to infraorbital nerve constriction injury.J Headache Pain. 2023 Oct 11;24(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01669-z. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37821818 Free PMC article.
-
Causal Relationship Between Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines and the Risk of Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Brain Behav. 2025 Apr;15(4):e70463. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70463. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40195053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao D. L., Zhang Z. J., Xie R. G., Jiang B. C., Ji R. R., Gao Y. J. (2014). Chemokine CXCL1 enhances inflammatory pain and increases NMDA receptor activity and COX-2 expression in spinal cord neurons via activation of CXCR2. Exp. Neurol. 261 328–336. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.05.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao Z., Xiong J., Takeuchi M., Kurama T., Goeddel D. V. (1996). TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 383 443–446. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

