Orbital Signaling in Graves' Orbitopathy
- PMID: 34899596
- PMCID: PMC8660111
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.739994
Orbital Signaling in Graves' Orbitopathy
Abstract
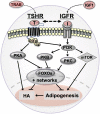
Graves' orbitopathy (GO) is a complex and poorly understood disease in which extensive remodeling of orbital tissue is dominated by adipogenesis and hyaluronan production. The resulting proptosis is disfiguring and underpins the majority of GO signs and symptoms. While there is strong evidence for the thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) being a thyroid/orbit shared autoantigen, the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) is also likely to play a key role in the disease. The pathogenesis of GO has been investigated extensively in the last decade with further understanding of some aspects of the disease. This is mainly derived by using in vitro and ex vivo analysis of the orbital tissues. Here, we have summarized the features of GO pathogenesis involving target autoantigens and their signaling pathways.
Keywords: IGF1R; TSAB; TSHR; adipogenesis; hyaluronan; thyroid eye disease.
Copyright © 2021 Draman, Zhang, Dayan and Ludgate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tanda ML, Piantanida E, Liparulo L, Veronesi G, Lai A, Sassi L, et al. . Prevalence and Natural History of Graves' Orbitopathy in a Large Series of Patients With Newly Diagnosed Graves' Hyperthyroidism Seen at a Single Center. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2013) 98(4):1443–9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3873 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crisp M, Starkey KJ, Lane C, Ham J, Ludgate M. Adipogenesis in Thyroid Eye Disease. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci (2000) 41(11):3249–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

