Graph Embedding Based Novel Gene Discovery Associated With Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 34899863
- PMCID: PMC8657768
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.779186
Graph Embedding Based Novel Gene Discovery Associated With Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
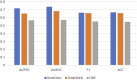
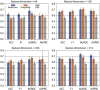
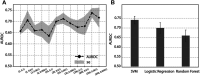
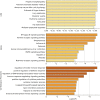
Diabetes mellitus is a group of complex metabolic disorders which has affected hundreds of millions of patients world-widely. The underlying pathogenesis of various types of diabetes is still unclear, which hinders the way of developing more efficient therapies. Although many genes have been found associated with diabetes mellitus, more novel genes are still needed to be discovered towards a complete picture of the underlying mechanism. With the development of complex molecular networks, network-based disease-gene prediction methods have been widely proposed. However, most existing methods are based on the hypothesis of guilt-by-association and often handcraft node features based on local topological structures. Advances in graph embedding techniques have enabled automatically global feature extraction from molecular networks. Inspired by the successful applications of cutting-edge graph embedding methods on complex diseases, we proposed a computational framework to investigate novel genes associated with diabetes mellitus. There are three main steps in the framework: network feature extraction based on graph embedding methods; feature denoising and regeneration using stacked autoencoder; and disease-gene prediction based on machine learning classifiers. We compared the performance by using different graph embedding methods and machine learning classifiers and designed the best workflow for predicting genes associated with diabetes mellitus. Functional enrichment analysis based on Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO), KEGG, and GO biological process and publication search further evaluated the predicted novel genes.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; disease gene prediction; graph embedding; molecular network; novel gene discovery.
Copyright © 2021 Du, Lin, Yuan, Chen, Liu and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Graph embedding-based link prediction for literature-based discovery in Alzheimer's Disease.J Biomed Inform. 2023 Sep;145:104464. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2023.104464. Epub 2023 Aug 2. J Biomed Inform. 2023. PMID: 37541406
-
Discovering Cerebral Ischemic Stroke Associated Genes Based on Network Representation Learning.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 1;12:728333. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.728333. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34539754 Free PMC article.
-
Graph embedding-based novel protein interaction prediction via higher-order graph convolutional network.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 24;15(9):e0238915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238915. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32970681 Free PMC article.
-
Data Integration Using Advances in Machine Learning in Drug Discovery and Molecular Biology.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2190:167-184. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0826-5_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32804365 Review.
-
To Embed or Not: Network Embedding as a Paradigm in Computational Biology.Front Genet. 2019 May 1;10:381. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00381. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31118945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Sequence Analysis landscape: A Systematic Review of Task Types, Databases, Datasets, Word Embeddings Methods, and Language Models.Database (Oxford). 2025 May 30;2025:baaf027. doi: 10.1093/database/baaf027. Database (Oxford). 2025. PMID: 40448683 Free PMC article.
-
Speos: an ensemble graph representation learning framework to predict core gene candidates for complex diseases.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 8;14(1):7206. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42975-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37938585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Dubayee M., Alshahrani A., Aljada D., Zahra M., Alotaibi A., Ababtain I., et al. (2021). Gene Expression Profiling of Apoptotic Proteins in Circulating Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Type II Diabetes Mellitus and Modulation by Metformin. Dmso 14, 1129–1139. 10.2147/dmso.s300048 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang C.-C., Lin C.-J. (2011). Libsvm. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2, 1–27. 10.1145/1961189.1961199 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

