Influence of Mindfulness and Relaxation on Treatment of Essential Hypertension: Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34900178
- PMCID: PMC8664515
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2272469
Influence of Mindfulness and Relaxation on Treatment of Essential Hypertension: Meta-Analysis
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Influence of Mindfulness and Relaxation on Treatment of Essential Hypertension: Meta-Analysis.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9781831. doi: 10.1155/2023/9781831. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37946912 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Some studies published previously have shown a strong correlation between hypertension and psychological nature including impulsion emotion or mindfulness and relaxation temperament, among which mindfulness and relaxation temperament might have a benign influence on blood pressure, ameliorating the hypertension. However, the conclusion was not confirmed.
Objective: The meta-analysis was performed to investigate the influence of mindfulness and relaxation on essential hypertension interventions and confirm the effects.
Methods: Systematic searches were conducted in common English and Chinese electronic databases (i.e., PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, CINAHL, PsycINFO, Cochrane Library, and Chinese Biomedical Literature Database) from 1980 to 2020. A meta-analysis including 5 studies was performed using Rev Man 5.4.1 software to estimate the influence of mindfulness and relaxation on blood pressure, ameliorating the hypertension. Publication bias and heterogeneity of samples were tested using a funnel plot. Studies were analyzed using either a random-effect model or a fixed-effect model.
Results: All the 5 studies investigated the influence of mindfulness and relaxation on diastolic and systolic blood pressure, with total 205 participants in the control group and 204 in the intervention group. The random-effects model (REM) was used to calculate the pooled effect for mindfulness and relaxation on diastolic blood pressure (I 2 = 0%, t 2 = 0.000, P=0.41). The random pooled effect size (MD) was 0.30 (95% CI = -0.81-1.42, P=0.59). REM was used to calculate the pooled effect for mindfulness and relaxation on systolic blood pressure (I 2 = 49%, t 2 = 3.05, P=0.10). The random pooled effect size (MD) was -1.05 (95% CI = -3.29-1.18, P=0.36). The results of this meta-analysis were influenced by publication bias to some degree.
Conclusion: All the results showed less influence of mindfulness and relaxation might act on diastolic or systolic blood pressure, when mindfulness and relaxation are used to intervene in treating CVD and hypertension.
Copyright © 2021 Fushun Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
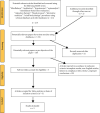



Similar articles
-
Effect of Meditation, Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction, and Relaxation Techniques as Mind-Body Medicine Practices to Reduce Blood Pressure in Cardiac Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Apr 17;16(4):e58434. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58434. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38765359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect and Acceptability of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Program on Patients With Elevated Blood Pressure or Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Hypertension. 2020 Dec;76(6):1992-2001. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16160. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 33131316
-
Effectiveness of the Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Program on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review of Literature.Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2018 Oct;15(5):344-352. doi: 10.1111/wvn.12319. Epub 2018 Aug 19. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2018. PMID: 30123977
-
The effect of nurse-led digital health interventions on blood pressure control for people with hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2023 Sep;55(5):1020-1035. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12882. Epub 2023 Mar 17. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2023. PMID: 36929538
-
Pulmonary Function in Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2022 Dec;20(10):606-617. doi: 10.1089/met.2022.0045. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 36125502
Cited by
-
Adverse Effects of Meditation: Autonomic Nervous System Activation and Individual Nauseous Responses During Samadhi Meditation in the Czech Republic.J Relig Health. 2024 Dec;63(6):4840-4860. doi: 10.1007/s10943-024-02024-5. Epub 2024 Apr 12. J Relig Health. 2024. PMID: 38605255 Free PMC article.
-
Lifestyle Interventions for Elevated Blood Pressure in Childhood-Approaches and Outcomes.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022 Nov;24(11):589-598. doi: 10.1007/s11906-022-01217-1. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022. PMID: 35972678 Review.
-
Designing a meditation module to affect etiological and preventive factors in primary hypertensive patients-A pilot study.Physiol Rep. 2025 Feb;13(3):e70226. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70226. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39916293 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Influence of Mindfulness and Relaxation on Treatment of Essential Hypertension: Meta-Analysis.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9781831. doi: 10.1155/2023/9781831. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37946912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elmer P. J., Obarzanek E., Vollmer W. M., et al. Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on diet, weight, physical fitness, and blood pressure control: 18-month results of a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine . 2006;144(7):p. 485. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-144-7-200604040-00007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

