Extradigital Glomus Tumor Mimics an Intrinsic Nerve Tumor in a Trauma Patient: Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 34900456
- PMCID: PMC8648149
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.19256
Extradigital Glomus Tumor Mimics an Intrinsic Nerve Tumor in a Trauma Patient: Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
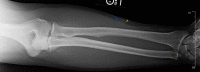
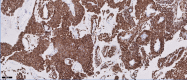
Glomus tumors are rare, painful, and usually benign neoplasms that typically occur at the subungual aspect of digits. Rarely, glomus tumors may arise in other areas of the body. We present a case of an extradigital glomus tumor on a forearm with prior trauma that presented with symptoms of an isolated peripheral neuropathy. Our review of literature reveals how upper or lower extremity glomus tumors can mimic neuropathies secondary to intrinsic nerve tumors (schwannoma, neurofibroma, or neuroma), radiculopathies, or manifestations of a complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). We emphasize the need to consider a broad differential diagnosis that includes glomus tumor when evaluating patients with painful dermal masses producing peripheral neuropathy or radiculopathy signs owing to the infiltrative growth pattern into or mass effect exerted on nearby nerves.
Keywords: extradigital glomus tumor; nerve tumor; peripheral neuropathy; trauma; traumatic neuroma.
Copyright © 2021, Ajala et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Extradigital glomus tumors: a 20-year experience. Schiefer TK, Parker WL, Anakwenze OA, Amadio PC, Inwards CY, Spinner RJ. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81:1337–1344. - PubMed
-
- Epineural glomus tumor of the posterior interosseous nerve: case report. Drabent P, Bielle F, Bernat I, Peyre M. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;74:232–234. - PubMed
-
- Extradigital glomic tumor of the forearm. About a case and review of literature. Lancien U, Duteille F, Perrot P. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2018;63:187–189. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
