Diabetic neuropathy: an insight on the transition from synthetic drugs to herbal therapies
- PMID: 34900824
- PMCID: PMC8630252
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-021-00830-2
Diabetic neuropathy: an insight on the transition from synthetic drugs to herbal therapies
Abstract
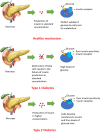
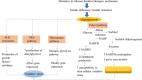
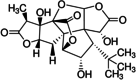
The global pandemic of prediabetes and diabetes has led to a severe corresponding complication of these disorders. Neuropathy is one of the most prevalent complication of diabetes is, affecting blood supply of the peripheral nervous system that may eventually results into loss of sensations, injuries, diabetic foot and death. The utmost identified risk of diabetic neuropathy is uncontrolled high blood glucose levels. However, aging, body mass index (BMI), oxidative stress, inflammation, increased HbA1c levels and blood pressure are among the other key factors involved in the upsurge of this disease. The so far treatment to deal with diabetic neuropathy is controlling metabolic glucose levels. Apart from this, drugs like reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibitors, aldose reductase inhibitors, PKC inhibitors, Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), anticonvulsants, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonists, are the other prescribed medications. However, the related side-effects (hallucinations, drowsiness, memory deficits), cost, poor pharmacokinetics and drug resistance brought the trust of patients down and thus herbal renaissance is occurring all over the word as the people have shifted their intentions from synthetic drugs to herbal remedies. Medicinal plants have widely been utilized as herbal remedies against number of ailments in Indian medicinal history. Their bioactive components are very much potent to handle different chronic disorders and complications with lesser-known side effects. Therefore, the current article mainly concludes the etiology and pathophysiology of diabetic neuropathy. Furthermore, it also highlights the important roles of medicinal plants and their naturally occurring bioactive compounds in addressing this disease.
Keywords: Bioactive compounds; Diabetes; Diabetic neuropathy; Herbal therapy; Medicinal plants; Peripheral nervous system; Traditional medicine.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Adapa D, Sarangi TK. A review on diabetes mellitus: complications, management and treatment modalities. J Med Health Sci. 2015; 4(3).
-
- Rottschäfer V. Analysis of glucose-insulin-glucagon interaction models. Bachelor thesis. Leiden University Mathematical Institute. 2017; 1–57.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

