Angiogenesis, Anti-Tumor, and Anti-Metastatic Activity of Novel α-Substituted Hetero-Aromatic Chalcone Hybrids as Inhibitors of Microtubule Polymerization
- PMID: 34900935
- PMCID: PMC8652888
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.766201
Angiogenesis, Anti-Tumor, and Anti-Metastatic Activity of Novel α-Substituted Hetero-Aromatic Chalcone Hybrids as Inhibitors of Microtubule Polymerization
Abstract
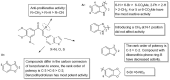
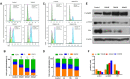
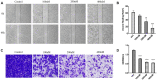
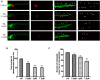
A library of new heteroaromatic ring-linked chalcone analogs were designed and synthesized of these, compound 7m with α-CH3 substitution and bearing a benzofuran ring, displaying the most potent activity, with IC50 values of 0.07-0.183 µM against three cancer cells. Its low cytotoxicity toward normal human cells and strong potency on drug-resistant cells revealed the possibility for cancer therapy. It also could moderately inhibit in vitro tubulin polymerization with an IC50 value of 12.23 µM, and the disruption of cellular architecture in MCF-7 cells was observed by an immunofluorescence assay. Cellular-based mechanism studies elucidated that 7m arrested the cell cycle at the G2/M phase and induced apoptosis by regulating the expression levels of caspases and PARP protein. Importantly, the compound 7 m was found to inhibit HUVEC tube formation, migration, and invasion in vitro. In vivo assay showed that 7m could effectively destroy angiogenesis of zebrafish embryos. Furthermore, our data suggested that treatment with 7m significantly reduced MCF-7 cell metastasis and proliferation in vitro and in zebrafish xenograft. Collectively, this work showed that chalcone hybrid 7m deserves further investigation as dual potential tubulin polymerization and angiogenesis inhibitor.
Keywords: angiogenesis; anti-tumor; chalcone analogs; microtubules; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Wang, Yuan, Zhao, Zhang, Yao and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of new 2-methoxyestradiol derivatives: Potent inhibitors of angiogenesis and tubulin polymerization.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Aug;113:104988. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104988. Epub 2021 May 13. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34034135
-
Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies of new chalcone derivatives containing diaryl ether moiety as potential anticancer agents and tubulin polymerization inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jan;95:103565. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103565. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 31927336
-
Synthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of Indole Triazole Conjugates as Microtubule Targeting Agents that are Effective against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(8):1047-1055. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200925102940. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32981511
-
Synthesis, Evaluation, and Mechanism Study of Novel Indole-Chalcone Derivatives Exerting Effective Antitumor Activity Through Microtubule Destabilization in Vitro and in Vivo.J Med Chem. 2016 Jun 9;59(11):5264-83. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00021. Epub 2016 May 23. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27149641
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of pyridine-chalcone derivatives as novel microtubule-destabilizing agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Jul 1;173:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 Apr 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30981112
Cited by
-
Chalcones and Gastrointestinal Cancers: Experimental Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 22;24(6):5964. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065964. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36983038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-angiogenic Potential of Trans-chalcone in an In Vivo Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Model: An ATP Antagonist to VEGFR with Predicted Blood-brain Barrier Permeability.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024;22(2):187-211. doi: 10.2174/0118715257250417231019102501. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37936455
-
Carbonic Anhydrase VIII (CAVIII) Gene Mediated Colorectal Cancer Growth and Angiogenesis through Mediated miRNA 16-5p.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 29;10(5):1030. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051030. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625769 Free PMC article.
-
BP-M345 as a Basis for the Discovery of New Diarylpentanoids with Promising Antimitotic Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 30;25(3):1691. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031691. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338967 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin Liposomes Combined with 5-Fluorouracil Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumor Growth of APC (Min/+) Mice and AOM/DSS-Induced Colorectal Cancer Mice.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Oct 27;17:5049-5061. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S373777. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36325149 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

