Multimodal imaging in pediatric uveitis
- PMID: 34901748
- PMCID: PMC8655435
- DOI: 10.1177/25158414211059244
Multimodal imaging in pediatric uveitis
Abstract
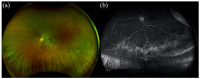
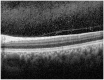
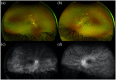
Pediatric uveitis accounts for up to 10% of all uveitis cases, so special attention must be paid to ensure early diagnosis as well as treatment and follow-up of these young patients in order to decrease the risk of possible ocular complications and consequently vision loss. Multimodal imaging has been an effective and important adjunct in the diagnoses and management of uveitis, especially in children. Reviewed here are the currently utilized modalities, advances, as well as their applications in juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis, pars planitis, retinal vasculitis, tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome, Behçet disease, Blau syndrome, and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome.
Keywords: fluorescein angiography; fundus photography; indocyanine green angiography; optical coherence tomography; uveitis.
© The Author(s), 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: The authors have no commercial or conflicting interests with the work published herein. Edmund Tsui receives research support from Kowa Company Ltd, Cylite Pty Ltd, Thrasher Research Fund, and the Knights Templar Eye Foundation. Fitz Gerald I. Diala receives support from UCLA Medical Scientist Training Program (NIH NIGMS grant GM008042).
Figures





References
-
- Sauberan DP. Pediatric uveitis. Int Ophthalmol Clin 2010; 50: 73–85. - PubMed
-
- Yang P, Zhong Z, Su G, et al. Retinal vasculitis, a common manifestation of idiopathic pediatric uveitis? Retina 2021; 41: 610–619. - PubMed
-
- Chan NSW, Choi J, Cheung CMG. Pediatric uveitis. Asia-Pacific J Ophthalmol 2018; 7: 192–199. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

