Clinical trials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and perspective
- PMID: 34901853
- PMCID: PMC8659356
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcab242
Clinical trials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and perspective
Abstract
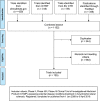
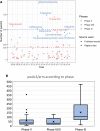
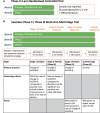
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a progressive and devastating neurodegenerative disease. Despite decades of clinical trials, effective disease-modifying drugs remain scarce. To understand the challenges of trial design and delivery, we performed a systematic review of Phase II, Phase II/III and Phase III amyotrophic lateral sclerosis clinical drug trials on trial registries and PubMed between 2008 and 2019. We identified 125 trials, investigating 76 drugs and recruiting more than 15 000 people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. About 90% of trials used traditional fixed designs. The limitations in understanding of disease biology, outcome measures, resources and barriers to trial participation in a rapidly progressive, disabling and heterogenous disease hindered timely and definitive evaluation of drugs in two-arm trials. Innovative trial designs, especially adaptive platform trials may offer significant efficiency gains to this end. We propose a flexible and scalable multi-arm, multi-stage trial platform where opportunities to participate in a clinical trial can become the default for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; clinical trials; methodology; perspective; systematic review.
© The Author(s) (2021). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures

References
-
- Westeneng H-J, Debray TPA, Visser AE, et al.Prognosis for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Development and validation of a personalised prediction model. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(5):423–433. - PubMed
-
- The Writing Group on behalf of the Edaravone (MCI-186) ALS 19 Study Group. Safety and efficacy of edaravone in well defined patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(7):505–512. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
