Digital Health Coaching for Type 2 Diabetes: Randomized Controlled Trial of Healthy at Home
- PMID: 34901926
- PMCID: PMC8655126
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2021.764735
Digital Health Coaching for Type 2 Diabetes: Randomized Controlled Trial of Healthy at Home
Abstract
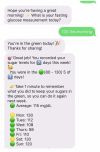
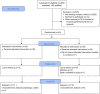
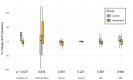
Digital health coaching is an intervention for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) that has potential to improve the quality of care for patients. Previous research has established the efficacy of digital interventions for behavior change. This pilot study addresses a research gap in finding effective and accessible behavioral interventions for under-resourced individuals with T2DM. We examined the impact of Healthy at Home, a 12-week phone and SMS-based (short message service) digital health coaching program, on insulin resistance which is an upstream marker for T2DM progression. We compared this intervention to usual diabetic care in a family medicine residency clinic in a randomized controlled trial. Digital health coaching significantly improved participants' calculated Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA2-IR) by -0.9 ± 0.4 compared with the control group (p = 0.029). This significance remained after controlling for years diagnosed with T2DM, enrollment in Medicaid, access to food, baseline stage of change, and race (p = 0.027). Increasing access to digital health coaching may lead to more effective control of diabetes for under-resourced patients. This study demonstrates the potential to implement a personalized, scalable, and effective digital health intervention to treat and manage T2DM through a lifestyle and behavioral approach to improve clinical outcomes (http://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT04872647).
Keywords: SMS-based; digital health; health coaching; lifestyle medicine; m-health; social determinants of health; stage-matched intervention; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2021 Azelton, Crowley, Vence, Underwood, Morris, Kelly and Landry.
Conflict of interest statement
KU is a founder of the non-profit organization CoachMe Health, which administers the digital health coaching program Healthy at Home. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kochanek KD, Xu J, Arias E. Mortality in the United States, 2019. National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department Of Health And Human Services; (2020). Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db395.htm (accessed July 31, 2021).
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

