Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Semaglutide and Liraglutide on Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER
- PMID: 34903039
- PMCID: PMC8860212
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055459
Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Semaglutide and Liraglutide on Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER
Abstract
Background: We assessed the effect of once-weekly semaglutide and once-daily liraglutide on kidney outcomes in type 2 diabetes.
Methods: Pooled (n=12 637) and by-trial data from SUSTAIN 6 (Trial to Evaluate Cardiovascular and Other Long-Term Outcomes With Semaglutide in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes; n=3297) and LEADER (Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results; n=9340) were assessed for albuminuria change, annual slope of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) change, and time to persistent eGFR reduction (30%, 40%, 50%, and 57%) from baseline.
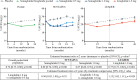
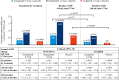
Results: The median follow-up durations were 2.1 years for SUSTAIN 6 and 3.8 years for LEADER. In the pooled analysis, semaglutide/liraglutide lowered albuminuria from baseline to 2 years after randomization by 24% versus placebo (95% CI, 20%-27%; P<0.001). Significant reductions were also observed in by-trial data analyses (P<0.001 for all), the largest being with semaglutide 1.0 mg (33% [95% CI, 24%-40%]; P<0.001) at 2 years. With semaglutide 1.0 mg and liraglutide, eGFR slope decline was significantly slowed by 0.87 and 0.26 mL/min/1.73 m2/y (P<0.0001 and P<0.001), respectively, versus placebo. Effects appeared larger in patients with baseline eGFR <60 versus ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (Pinteraction=0.06 and 0.008 for semaglutide 1.0 mg and liraglutide, respectively). Semaglutide/liraglutide significantly lowered risk of persistent 40% and 50% eGFR reductions versus placebo (hazard ratio [HR], 0.86 [95% CI, 0.75-0.99]; P=0.039 and HR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.66-0.97]; P=0.023, respectively). Similar, nonsignificant, directional results were observed for 30% and 57% eGFR reductions (HR, 0.92 [95% CI, 0.84-1.02]; P=0.10 and HR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.69-1.13]; P=0.34). In patients with baseline eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, the likelihood of persistent reduction for all thresholds was increased, ranging from HR 0.71 for 30% reduction (95% CI, 0.59-0.85; P=0.0003, Pinteraction=0.017) to 0.54 for 57% reduction (95% CI, 0.36-0.81; P=0.003, Pinteraction=0.035).
Conclusions: In patients with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide/liraglutide offered kidney-protective effects, which appeared more pronounced in patients with preexisting chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; eGFR; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; liraglutide; semaglutide; type 2 diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- Roglic G. WHO Global report on diabetes: a summary. Int J Noncommun Dis. 2016;1:3–8.
-
- Liyanage T, Ninomiya T, Jha V, Neal B, Patrice HM, Okpechi I, Zhao MH, Lv J, Garg AX, Knight J, et al. . Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet. 2015;385:1975–1982. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61601-9 - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System. Annual data report: chapter 7: healthcare expenditures for persons with CKD. Published 2018. Accessed November 7, 2021. https://www.usrds.org/media/1718/v1_c07_ckd_costs_18_usrds.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

