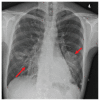
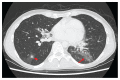
Pneumonie lipoïde exogène associée à des produits oraux et intranasaux à base d’huile
- PMID: 34903596
- PMCID: PMC8677575
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.210439-f
Pneumonie lipoïde exogène associée à des produits oraux et intranasaux à base d’huile
Conflict of interest statement
Intérêts concurrents: Aucun déclaré.
Figures


References
-
- Arancibia F, Bauer TT, Ewig S, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia due to gramnegative bacteria and pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162:1849–58. - PubMed
-
- Low DE, Mazzulli T, Marrie T. Progressive and nonresolving pneumonia. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2005;11:247–52. - PubMed
-
- Johnson J. Slowly resolving and nonresolving pneumonias. Questions to ask when response is delayed. Postgrad Med 2000;108:15–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
