Newly discovered endocrine functions of the liver
- PMID: 34904032
- PMCID: PMC8637678
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1611
Newly discovered endocrine functions of the liver
Abstract
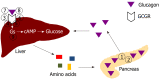
The liver, the largest solid visceral organ of the body, has numerous endocrine functions, such as direct hormone and hepatokine production, hormone metabolism, synthesis of binding proteins, and processing and redistribution of metabolic fuels. In the last 10 years, many new endocrine functions of the liver have been discovered. Advances in the classical endocrine functions include delineation of mechanisms of liver production of endocrine hormones [including 25-hydroxyvitamin D, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and angiotensinogen], hepatic metabolism of hormones (including thyroid hormones, glucagon-like peptide-1, and steroid hormones), and actions of specific binding proteins to glucocorticoids, sex steroids, and thyroid hormones. These studies have furthered insight into cirrhosis-associated endocrinopathies, such as hypogonadism, osteoporosis, IGF-1 deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, alterations in glucose and lipid homeostasis, and controversially relative adrenal insufficiency. Several novel endocrine functions of the liver have also been unraveled, elucidating the liver's key negative feedback regulatory role in the pancreatic α cell-liver axis, which regulates pancreatic α cell mass, glucagon secretion, and circulating amino acid levels. Betatrophin and other hepatokines, such as fetuin-A and fibroblast growth factor 21, have also been discovered to play important endocrine roles in modulating insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and body weight. It is expected that more endocrine functions of the liver will be revealed in the near future.
Keywords: Amino acids; Endocrine function; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Hepatokine; Hormone; Liver.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Both authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Watt MJ, Miotto PM, De Nardo W, Montgomery MK. The Liver as an Endocrine Organ-Linking NAFLD and Insulin Resistance. Endocr Rev. 2019;40:1367–1393. - PubMed
-
- Grant DM. Detoxification pathways in the liver. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1991;14:421–430. - PubMed
-
- Malespin M, Nassri A. Endocrine Diseases and the Liver: An Update. Clin Liver Dis. 2019;23:233–246. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

