How young people experienced COVID-19 disease containment measures in the Western Cape, South Africa: A qualitative study including the perspectives of young people, their parents, teachers and school counsellors
- PMID: 34904360
- PMCID: PMC9300161
- DOI: 10.1111/papt.12374
How young people experienced COVID-19 disease containment measures in the Western Cape, South Africa: A qualitative study including the perspectives of young people, their parents, teachers and school counsellors
Abstract
Background: Little is known about the potential impact of COVID-19 disease containment measures on children's mental health and well-being, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. We sought to explore this amongst young adolescents in South Africa and from the perspectives of multiple key stakeholders.
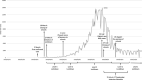
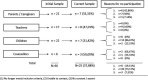
Methods: We conducted 25 individual semi-structured telephonic interviews with children (n = 7, aged 12-13 years), teachers (n = 8), parents/caregivers (n = 7) and school counsellors (n = 3) from two public primary schools in the Western Cape, South Africa. Interviews were conducted between July and September 2020 and transcribed verbatim. The data were analysed inductively using thematic analysis procures.
Results: We generated three overarching themes: "locked down at home", "social disconnection" and "back to school." Children had varying reactions to COVID-19 and lockdown including excitement, frustration, anxiety, boredom and loneliness. Parents were anxious about teaching, and technology did not consistently provide the necessary support. Children felt disconnected from their peers at home, and at school, reconnecting with friends was obstructed by disease containment measures. All participants were concerned about children completing the academic year successfully and worried excessively about the implications of this year on their future.
Conclusion: Young people and their immediate networks, in a low- and middle-income context, described a variety of negative impacts of disease containment measures emotionally, although there was a wide variety of experiences. Children, parents, teachers and counsellors all wanted resources and support and were concerned about the longer-term impacts of disease containment measures.
Keywords: COVID-19; LMICs; South Africa; adolescents; disease containment measures; mental health; pandemic; qualitative.
© 2021 The Authors. Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The British Psychological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) have declared that they have no competing or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdulah, D. M. , Abdulla, B. M. O. , & Liamputtong, P. (2020). Psychological response of children to home confinement during COVID‐19: A qualitative arts‐based research. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 002076402097243. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0020764020972439 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braun, V. , Clarke, V. , Hayfield, N. , & Terry, G. (2019). Handbook of research methods in health and social sciences. In Liamputtong P. (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in health and social sciences (pp. 843–860). Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical