Identification and validation of a novel pathogenic variant in GDF2 (BMP9) responsible for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and pulmonary arteriovenous malformations
- PMID: 34904380
- PMCID: PMC9939255
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62584
Identification and validation of a novel pathogenic variant in GDF2 (BMP9) responsible for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and pulmonary arteriovenous malformations
Abstract
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant multisystemic vascular dysplasia, characterized by arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), mucocutaneous telangiectasia and nosebleeds. HHT is caused by a heterozygous null allele in ACVRL1, ENG, or SMAD4, which encode proteins mediating bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling. Several missense and stop-gain variants identified in GDF2 (encoding BMP9) have been reported to cause a vascular anomaly syndrome similar to HHT, however none of these patients met diagnostic criteria for HHT. HHT families from UK NHS Genomic Medicine Centres were recruited to the Genomics England 100,000 Genomes Project. Whole genome sequencing and tiering protocols identified a novel, heterozygous GDF2 sequence variant in all three affected members of one HHT family who had previously screened negative for ACVRL1, ENG, and SMAD4. All three had nosebleeds and typical HHT telangiectasia, and the proband also had severe pulmonary AVMs from childhood. In vitro studies showed the mutant construct expressed the proprotein but lacked active mature BMP9 dimer, suggesting the mutation disrupts correct cleavage of the protein. Plasma BMP9 levels in the patients were significantly lower than controls. In conclusion, we propose that this heterozygous GDF2 variant is a rare cause of HHT associated with pulmonary AVMs.
Keywords: arteriovenous malformations; bone morphogenetic protein 9; hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
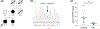
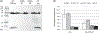
References
-
- Criteria Committee New York Heart Association Inc. (1964). Diseases of the heart and blood vessels: Nomenclature and criteria for diagnosis (6th ed.) p. 114. Boston: Little, Brown & Co.
-
- David L, Mallet C, Mazerbourg S, Feige JJ, & Bailly S (2007). Identification of BMP9 and BMP10 as functional activators of the orphan activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells. Blood, 109, 1953–1961. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher CM (1960). Standardised questionnaire on respiratory symptoms: A statement prepared and approved by the MRC Committee on the aetiology of chronic bronchitis (MRC breathlessness score). BMJ, 2, 1665. - PubMed
-
- Gallione CJ, Repetto GM, Legius E, Rustgi AK, Schelley SL, Tejpar S, Mitchell G, Drouin E, Westermann CJJ, & Marchuk DA (2004). A combined syndrome of juvenile polyposis and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with mutations in MADH4 (SMAD4). Lancet, 363, 852–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

