Inhibitory pattern recognition receptors
- PMID: 34905019
- PMCID: PMC8674843
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20211463
Inhibitory pattern recognition receptors
Abstract
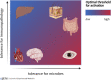
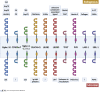
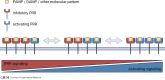
Pathogen- and damage-associated molecular patterns are sensed by the immune system's pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) upon contact with a microbe or damaged tissue. In situations such as contact with commensals or during physiological cell death, the immune system should not respond to these patterns. Hence, immune responses need to be context dependent, but it is not clear how context for molecular pattern recognition is provided. We discuss inhibitory receptors as potential counterparts to activating pattern recognition receptors. We propose a group of inhibitory pattern recognition receptors (iPRRs) that recognize endogenous and microbial patterns associated with danger, homeostasis, or both. We propose that recognition of molecular patterns by iPRRs provides context, helps mediate tolerance to microbes, and helps balance responses to danger signals.
© 2021 Rumpret et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: L. Meyaard reported grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, NextCure, and NGM Biopharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Innate Immune Memory and the Host Response to Infection.J Immunol. 2022 Feb 15;208(4):785-792. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101058. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35115374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Chaos to Harmony: Responses and Signaling upon Microbial Pattern Recognition.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2017 Aug 4;55:109-137. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080516-035649. Epub 2017 May 19. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2017. PMID: 28525309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOD-Like Receptors: Guards of Cellular Homeostasis Perturbation during Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 23;22(13):6714. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136714. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidation-specific epitopes are danger-associated molecular patterns recognized by pattern recognition receptors of innate immunity.Circ Res. 2011 Jan 21;108(2):235-48. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223875. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21252151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The crosstalk between pattern-recognition receptor signaling and calcium signaling.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 1;192:745-756. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.014. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34634335 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting circulating high mobility group box-1 and histones by extracorporeal blood purification as an immunomodulation strategy against critical illnesses.Crit Care. 2023 Feb 28;27(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04382-0. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 36855150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunosuppression in Sepsis: Biomarkers and Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 13;12(1):175. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010175. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothesis: hematogenous metastatic cancer cells of solid tumors may disguise themselves as memory macrophages for metastasis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 5;14:1412296. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1412296. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39035733 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal pyroptosis and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases.Inflamm Res. 2023 Sep;72(9):1839-1859. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01790-4. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37725102 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Regulation of Macrophages in Innate Immunity and Diverse Roles of Macrophages During Cochlear Inflammation.Neurosci Bull. 2024 Feb;40(2):255-267. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01085-y. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Neurosci Bull. 2024. PMID: 37391607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez, Y., Tang X., Coligan J.E., and Borrego F.. 2008. The CD300a (IRp60) inhibitory receptor is rapidly up-regulated on human neutrophils in response to inflammatory stimuli and modulates CD32a (FcgammaRIIa) mediated signaling. Mol. Immunol. 45:253–258. 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.05.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angata, T., Kerr S.C., Greaves D.R., Varki N.M., Crocker P.R., and Varki A.. 2002. Cloning and characterization of human Siglec-11. A recently evolved signaling molecule that can interact with SHP-1 and SHP-2 and is expressed by tissue macrophages, including brain microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 277:24466–24474. 10.1074/jbc.M202833200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arakawa, S., Suzukawa M., Ohshima N., Tashimo H., Asari I., Matsui H., Kobayashi N., Shoji S., Nagase T., and Ohta K.. 2018. Expression of Siglec-8 is regulated by interleukin-5, and serum levels of soluble Siglec-8 may predict responsiveness of severe eosinophilic asthma to mepolizumab. Allergol. Int. 67S:S41–S44. 10.1016/j.alit.2018.03.006 - DOI - PubMed

