Detection of the sentinel lymph node with hybrid tracer (ICG-[99mTc]Tc-albumin nanocolloid) in intermediate- and high-risk endometrial cancer: a feasibility study
- PMID: 34905122
- PMCID: PMC8671586
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-021-00863-x
Detection of the sentinel lymph node with hybrid tracer (ICG-[99mTc]Tc-albumin nanocolloid) in intermediate- and high-risk endometrial cancer: a feasibility study
Abstract
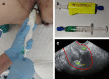
Purpose: Indocyanine green (ICG) is frequently used for the detection of the sentinel lymph node (SLN) in gynecology, but it carries the loss of the presurgical SLN mapping provided by [99mTc]-based colloids. Hybrid tracers such as ICG-[99mTc]Tc-albumin nanocolloid combine the benefits of both components. The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility and applicability of this hybrid tracer injected by transvaginal ultrasound-guided myometrial injection of radiotracer (TUMIR) approach in the detection of SLNs in patients with intermediate- and high-risk EC.
Methods: Fifty-two patients with intermediate- and high-risk EC underwent SLN biopsy after injection of a hybrid tracer using the TUMIR approach, followed by pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy. SLNs were detected preoperatively by lymphoscintigraphic study and intraoperatively by gamma probe and near-infrared (NIR) optical laparoscopic camera.
Results: Preoperative lymphatic drainage was obtained in 69% and intraoperative detection in 71.4% of patients. A total of 146 SLNs (4.17 SLNs/patient) were biopsied. Pelvic bilateral detection was observed in 57% of the women and paraaortic drainage in 34% of the patients. The radioactive component allowed the detection of SLN in 97.1% of the patients, while the fluorescent component detected 80%. In more than 17% of the patients with intraoperative detection, SLNs were detected only by the radioactive signal. Lymph node metastasis was identified in 14.3% of patients submitted to SLNB. The sensitivity and negative predictive value for metastatic involvement were 100%.
Conclusion: TUMIR injection of a hybrid tracer in patients with intermediate- and high-risk EC combines the benefits of the radiotracer and the fluorescence methods with a single tracer. The method increases the paraaortic detection rate and allows a potential increase in SLN detection. Notwithstanding, based on our findings, the radioactive component of the hybrid tracer cannot be obviated.
Keywords: Endometrial cancer; Hybrid tracer (ICG-[99mTc]Tc-albumin nanocolloid); ICG; Lymphatic mapping; Radiotracer; Sentinel lymph node.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Concomitant radio- and fluorescence-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity using ICG-(99m)Tc-nanocolloid.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012 Jul;39(7):1128-36. doi: 10.1007/s00259-012-2129-5. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22526966 Clinical Trial.
-
Paraaortic sentinel lymph node detection in intermediate and high-risk endometrial cancer by transvaginal ultrasound-guided myometrial injection of radiotracer (TUMIR).J Gynecol Oncol. 2021 Jul;32(4):e52. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2021.32.e52. Epub 2021 Mar 20. J Gynecol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33908710 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a radioactive and fluorescent hybrid tracer for sentinel lymph node biopsy in head and neck malignancies: prospective randomized clinical trial to compare ICG-(99m)Tc-nanocolloid hybrid tracer versus (99m)Tc-nanocolloid.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Oct;42(11):1631-1638. doi: 10.1007/s00259-015-3093-7. Epub 2015 May 31. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26025245 Clinical Trial.
-
Indocyanine green versus technetium-99m with blue dye for sentinel lymph node detection in early-stage cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022 Jan;5(1):e1401. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1401. Epub 2021 May 11. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 33973745 Free PMC article.
-
Sentinel node mapping with indocyanine green and endoscopic near-infrared fluorescence imaging in endometrial cancer. A pilot study and review of the literature.Gynecol Oncol. 2015 Jun;137(3):443-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Gynecol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25771495 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular image-guided surgery in gynaecological cancer: where do we stand?Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Aug;51(10):3026-3039. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06604-1. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38233609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictors of Bilateral SLN Radiocolloid Detection in Endometrial Carcinoma.World J Nucl Med. 2023 Dec 26;22(4):261-266. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1777693. eCollection 2023 Dec. World J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 38152100 Free PMC article.
-
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Endometrial Cancer: Dual Injection, Dual Tracer-A Multidisciplinary Exhaustive Approach to Nodal Staging.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 13;14(4):929. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040929. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205676 Free PMC article.
-
Robotically assisted augmented reality system for identification of targeted lymph nodes in laparoscopic gynecological surgery: a first step toward the identification of sentinel node : Augmented reality in gynecological surgery.Surg Endosc. 2022 Dec;36(12):9224-9233. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09409-1. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Surg Endosc. 2022. PMID: 35831676
-
Steerable DROP-IN radioguidance during minimal-invasive non-robotic cervical and endometrial sentinel lymph node surgery.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Aug;51(10):3089-3097. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06589-3. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38233608 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Abu-Rustum NR, Yashar CM, Bradley K, et al. NCCN Guidelines. Uterine Neoplasms Version 1.2021; 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

