Myristicin regulates proliferation and apoptosis in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-stimulated human vascular smooth muscle cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway
- PMID: 34905418
- PMCID: PMC8676624
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2021.2010775
Myristicin regulates proliferation and apoptosis in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-stimulated human vascular smooth muscle cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway
Abstract
Context: Atherosclerosis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease. Human vascular smooth muscle cell (hVSMC) accumulation and human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) dysfunction are associated with the pathogenesis of AS. This study explores whether myristicin plays a protective role in AS.
Materials and methods: hVSMCs and HUVECs were stimulated with 100 μg/mL oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) to establish a cellular model of AS. Cell viability, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and cell apoptosis were evaluated using MTT, LDH and flow cytometry assays, respectively. Cell migration and inflammatory cytokine release were assessed using Transwell assay and ELISA.
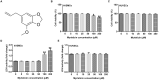
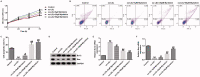
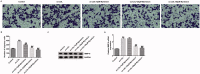
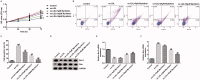
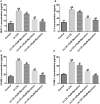
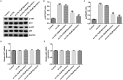
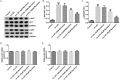
Results: Myristicin (5, 10, 25, and 50 μM) had no obvious effect on cell viability or the activity of LDH in hVSMCs, while 100 and 200 μM myristicin markedly suppressed hVSMCs viability and increased LDH release. Myristicin had no obvious effect on cell viability or the activity of LDH in HUVECs. Myristicin inhibited viability and increased apoptosis in ox-LDL-treated hVSMCs, but was associated with increased proliferation and inhibited apoptosis in HUVECs stimulated by ox-LDL. Additionally, myristicin markedly suppressed ox-LDL-induced hVSMCs migration and the release of inflammatory cytokines, including MCP-1, IL-6, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, in HUVECs. Results also demonstrated that the promoting effects of ox-LDL on the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signalling pathway in both hVSMCs and HUVECs were abolished by treatment with myristicin.
Discussion and conclusions: Myristicin regulated proliferation and apoptosis by regulating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway in ox-LDL-stimulated hVSMCs and HUVECs. Thus, myristicin may be used as a new potential drug for AS treatment.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; atherosclerosis; inflammation; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Cao Z, Xia W, Zhang X, Yuan H, Guan D, Gao L.. 2020. Hepatotoxicity of nutmeg: a pilot study based on metabolomics. Biomed Pharmacother. 131:110780. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
