Health Insurance Literacy and Medical Debt in Middle-Age Americans
- PMID: 34905430
- PMCID: PMC8668166
- DOI: 10.3928/24748307-20211102-01
Health Insurance Literacy and Medical Debt in Middle-Age Americans
Abstract
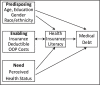
Background: Health insurance literacy (HIL) may influence medical financial burden among people who are sick and the most vulnerable.
Objective: This study examined the relationships between HIL, health insurance factors, and medical debt among middle-age Americans, a population with an increasing prevalence of illnesses.
Methods: Linear and generalized linear regression analyses were conducted on data drawn from the 2015-2016 waves of the Health Reform Monitoring Survey, a national, internet-based sample of Americans age 18 to 64 years. The analytical sample included 8,042 people age 50 to 64 years.
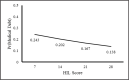
Key results: Adjusted mean HIL scores did not differ by private versus public insurance or by out-of-pocket costs. Mean HIL scores were lower with higher deductibles; however, differences in mean scores were small. Higher HIL was associated with lower medical debt (odds ratio = 0.97; 95% confidence interval [0.96, 0.98]), but at the highest HIL score, the risk of having medical debt was still 13.8%. Public coverage, higher annual deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs were associated with higher risks of having medical debt.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that HIL plays an important role in medical debt burden. However, with the shift toward high cost-sharing insurance plans, addressing health care affordability issues along with HIL are critical to eliminate medical debt problems. [HLRP: Health Literacy Research and Practice. 2021;5(4):e319-e332.] Plain Language Summary: Understanding and using health insurance (also defined as health insurance literacy) may influence the ability to pay medical bills among people who are sick and vulnerable. This study examined the relationships among health insurance literacy, health insurance factors, and difficulty paying medical bills (i.e., medical debt) in Americans age 50 to 64 years using data from the Health Reform Monitoring Survey. People with higher health insurance literacy reported lower medical debt. Type of insurance coverage did not influence medical debt. Those with annual deductibles and out-of-pocket health care costs were more likely to report having medical debt.
Figures
References
-
- Bartholomae , S. , Russell , M. B. , Braun , B. , & McCoy , T. ( 2016. ). Building health insurance literacy: Evidence from the Smart Choice Health Insurance (TM) program . Journal of Family and Economic Issues , 37 ( 2 ), 140 – 155 . 10.1007/s10834-016-9482-7 - DOI
-
- Bhargava , S. , Loewenstein , G. , & Sydnor , J. ( 2017. ). Choose to lose: Health plan choices from a menu with dominated options . The Quarterly Journal of Economics , 132 ( 3 ), 1319 – 1372 . 10.1093/qje/qjx011 - DOI
-
- Braga , B. , McKernan , S. M. , & Karas , A . ( 2017. , March ). Is financial knowledge associated with past-due medical debt? Urban Institute; . https://www.urban.org/sites/default/files/publication/88591/financial_kn...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

