Prognostic value of CDCA3 in kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34905505
- PMCID: PMC8714141
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203767
Prognostic value of CDCA3 in kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma
Abstract
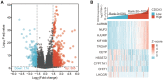
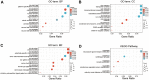
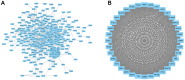
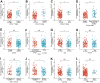
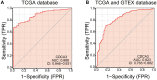
Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma (KIRP) is a type of low-grade malignant renal cell carcinoma. Huge challenges remain in the treatment of KIRP. Cell division cycle associated 3 (CDCA3) participates in human physiological and pathological processes. However, its role in KIRP has not been established. Here, we evaluated the prognostic value of CDCA3 in KIRP using a comprehensive bioinformatics approach. Data for CDCA3 expression in KIRP were obtained from online database. Different expression genes between high and low CDCA3 expression groups were identified and evaluated by performing Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analyses. A gene set enrichment analysis was performed to elucidate the function and pathway differences between the different. Differences in immune cell infiltration between low and high CDCA3 expression groups were analyzed by a single-sample GSEA method for immune cells. A protein-protein interaction network was generated and hub genes were identified. UALCAN was used to analyze associations between the mRNA expression levels of CDCA3 in KIRP tissues with clinicopathologic parameters. The diagnostic efficacy of CDCA3 for KIRP was analyzed by ROC analysis. Logistic regression was used to analyze relationships between the clinicopathological characteristics and CDCA3 expression. Our results indicated that high CDCA3 mRNA expression is significantly associated with some clinicopathologic parameters in KIRP patients High CDCA3 mRNA expression associated with a shorter overall survival, progression-free interval, and disease-special survival. Taken together, CDCA3 is a potential target for the development of anti-KIRP therapeutics and is an efficient prognostic marker.
Keywords: cell division cycle associated 3; differential expression; immune cell infiltration; kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; prognostic values.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bioinformatic analysis highlights SNHG6 as a putative prognostic biomarker for kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma.BMC Urol. 2023 Apr 1;23(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01218-5. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 37004005 Free PMC article.
-
Construction autophagy-related prognostic risk signature combined with clinicopathological validation analysis for survival prediction of kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2021 Apr 15;21(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08139-2. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33858375 Free PMC article.
-
PYCR in Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma: Expression, Prognosis, Gene Regulation Network, and Regulation Targets.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Dec 28;27(12):336. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2712336. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36624948
-
Cell Division Cycle-Associated Protein 3 (CDCA3) Is a Potential Biomarker for Clinical Prognosis and Immunotherapy in Pan-Cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Aug 30;2022:4632453. doi: 10.1155/2022/4632453. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9870382. doi: 10.1155/2023/9870382. PMID: 36082153 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic tissuemarkers in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2010;7(6):261-8. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2010-0195. Cancer Biomark. 2010. PMID: 21694464 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive molecular analyses and experimental validation of CDCAs with potential implications in kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma prognosis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 13;10(12):e33045. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33045. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38988558 Free PMC article.
-
CDCA3 is a prognostic biomarker for cutaneous melanoma and is connected with immune infiltration.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 11;12:1055308. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1055308. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36713580 Free PMC article.
-
CDCA3 Predicts Poor Prognosis and Affects CD8+ T Cell Infiltration in Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;2022:6343760. doi: 10.1155/2022/6343760. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36213833 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of cell division cycle-associated protein-3 in prostate cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 8;102(36):e34655. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034655. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37682152 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying CDCA3 as a pivotal biomarker for predicting outcomes and immunotherapy efficacy in pan-renal cell carcinoma.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):1955-1970. doi: 10.21037/tau-24-233. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 39434731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Little RA, Jamin Y, Boult JK, Naish JH, Watson Y, Cheung S, Holliday KF, Lu H, McHugh DJ, Irlam J, West CM, Betts GN, Ashton G, et al.. Mapping Hypoxia in Renal Carcinoma with Oxygen-enhanced MRI: Comparison with Intrinsic Susceptibility MRI and Pathology. Radiology. 2018; 288:739–47. 10.1148/radiol.2018171531 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armstrong AJ, Halabi S, Eisen T, Broderick S, Stadler WM, Jones RJ, Garcia JA, Vaishampayan UN, Picus J, Hawkins RE, Hainsworth JD, Kollmannsberger CK, Logan TF, et al.. Everolimus versus sunitinib for patients with metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ASPEN): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016; 17:378–88. 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00515-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tannir NM, Jonasch E, Albiges L, Altinmakas E, Ng CS, Matin SF, Wang X, Qiao W, Dubauskas Lim Z, Tamboli P, Rao P, Sircar K, Karam JA, et al.. Everolimus Versus Sunitinib Prospective Evaluation in Metastatic Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ESPN): A Randomized Multicenter Phase 2 Trial. Eur Urol. 2016; 69:866–74. 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.10.049 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Linehan WM, Spellman PT, Ricketts CJ, Creighton CJ, Fei SS, Davis C, Wheeler DA, Murray BA, Schmidt L, Vocke CD, Peto M, Al Mamun AA, Shinbrot E, et al., and Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Papillary Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:135–45. 10.1056/NEJMoa1505917 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

