DamID transcriptional profiling identifies the Snail/Scratch transcription factor Kahuli as an Alk target in the Drosophila visceral mesoderm
- PMID: 34905617
- PMCID: PMC8722224
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.199465
DamID transcriptional profiling identifies the Snail/Scratch transcription factor Kahuli as an Alk target in the Drosophila visceral mesoderm
Abstract
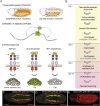
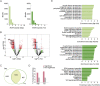
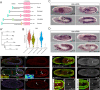
Development of the Drosophila visceral muscle depends on Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (Alk) receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling, which specifies founder cells (FCs) in the circular visceral mesoderm (VM). Although Alk activation by its ligand Jelly Belly (Jeb) is well characterized, few target molecules have been identified. Here, we used targeted DamID (TaDa) to identify Alk targets in embryos overexpressing Jeb versus embryos with abrogated Alk activity, revealing differentially expressed genes, including the Snail/Scratch family transcription factor Kahuli (Kah). We confirmed Kah mRNA and protein expression in the VM, and identified midgut constriction defects in Kah mutants similar to those of pointed (pnt). ChIP and RNA-Seq data analysis defined a Kah target-binding site similar to that of Snail, and identified a set of common target genes putatively regulated by Kah and Pnt during midgut constriction. Taken together, we report a rich dataset of Alk-responsive loci in the embryonic VM and functionally characterize the role of Kah in the regulation of embryonic midgut morphogenesis.
Keywords: ChIP; ETS; Jelly belly; Midgut constriction; Pointed; Signaling; Single cell; TaDa.
© 2021. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Jeb/Alk signalling regulates the Lame duck GLI family transcription factor in the Drosophila visceral mesoderm.Development. 2013 Aug;140(15):3156-66. doi: 10.1242/dev.094466. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Development. 2013. PMID: 23824577
-
Jeb signals through the Alk receptor tyrosine kinase to drive visceral muscle fusion.Nature. 2003 Oct 2;425(6957):512-6. doi: 10.1038/nature01950. Nature. 2003. PMID: 14523447
-
Myoblast determination in the somatic and visceral mesoderm depends on Notch signalling as well as on milliways(mili(Alk)) as receptor for Jeb signalling.Development. 2004 Feb;131(4):743-54. doi: 10.1242/dev.00972. Development. 2004. PMID: 14757637
-
Diversification of muscle types in Drosophila embryos.Exp Cell Res. 2022 Jan 1;410(1):112950. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112950. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 34838813 Review.
-
Lessons from Drosophila Pointed, an ETS family transcription factor and key nuclear effector of the RTK signaling pathway.Genesis. 2018 Dec;56(11-12):e23257. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23257. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Genesis. 2018. PMID: 30318758 Review.
Cited by
-
An endogenous cluster of target-directed microRNA degradation sites induces decay of distinct microRNA families.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 13:2024.12.11.627053. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.11.627053. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2025 Aug 19;44(9):116162. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116162. PMID: 39713366 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Visceral organ morphogenesis via calcium-patterned muscle constrictions.Elife. 2022 May 20;11:e77355. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77355. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35593701 Free PMC article.
-
The Alk receptor tyrosine kinase regulates Sparkly, a novel activity regulating neuropeptide precursor in the Drosophila central nervous system.Elife. 2024 Jun 21;12:RP88985. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88985. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38904987 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

