Effect of Intermittent Fasting on Glucose Homeostasis and Bone Remodeling in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Rat Model
- PMID: 34905677
- PMCID: PMC8671024
- DOI: 10.11005/jbm.2021.28.4.307
Effect of Intermittent Fasting on Glucose Homeostasis and Bone Remodeling in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Rat Model
Abstract
Background: The present study examined the effect of intermittent fasting (IF) on bone mineral content (BMC) and bone mineral density (BMD) and the markers of bone remodeling in a glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIO) rat model.
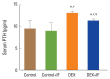
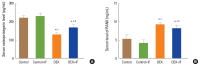
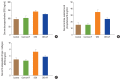
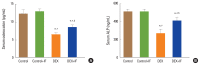
Methods: Forty male rats were allocated to 4 groups (N=10 per group): control group of normal rats; control+IF group (normal rats subjected to IF for 16-18 hr daily for 90 days); dexamethasone (DEX) group: (DEX [0.5 mg i.p.] for 90 days); and DEX+IF group (DEX and IF for 90 days). By the end of the experiment, BMD and BMC in the right tibia were measured. Serum levels of the following were measured: glucose; insulin; triglycerides (TGs); total cholesterol; parathyroid hormone (PTH); osteoprotegerin (OPG); receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB (RANK); bone-resorbing cytokines, including bone deoxypyridinoline (DPD), N-terminal telopeptide of collagen type I (NTX-1), and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b (TRAP-5b); and bone-forming cytokines, including alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and osteocalcin (OC).
Results: DEX administration for 90 days resulted in significantly increased serum levels of glucose, insulin, TGs, cholesterol, PTH, OPG, DPD, NTX-1, and TRAP-5b and significantly decreased BMD, BMC, and serum levels of RANK, OC, and ALP (all P<0.05). IF for 90 days significantly improved all these parameters (all P<0.05).
Conclusions: IF corrected GIO in rats by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and PTH secretion and stimulating osteoblast activity.
Keywords: Bone remodeling; Fasting; Glucocorticoids; Osteocalcin; Osteoporosis; Parathyroid hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
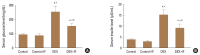



Similar articles
-
Impact of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Mineral Content in a Rat Model of Male Hypogonadism.Vet Sci. 2020 Nov 23;7(4):185. doi: 10.3390/vetsci7040185. Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33238425 Free PMC article.
-
In Rats, Whole and Refined Grains Decrease Bone Mineral Density and Content through Modulating Osteoprotegerin and Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 10;11(6):1686. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061686. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371781 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclastic function is accelerated in male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the preventive role of osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor/osteoprotegerin (OCIF/OPG) on the decrease of bone mineral density.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005 May;68(2):117-25. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2004.08.006. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005. PMID: 15860239
-
Resveratrol Modulates Bone Mineral Density and Bone Mineral Content in A Rat Model of Male Hypogonadism.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Feb;29(2):146-154. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-2895-2. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 35799086
-
Bone remodelling markers in rheumatoid arthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:484280. doi: 10.1155/2014/484280. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24839355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The ATF3-OPG Axis Contributes to Bone Formation by Regulating the Differentiation of Osteoclasts, Osteoblasts, and Adipocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 23;23(7):3500. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073500. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408860 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary trends and obesity in Saudi Arabia.Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 11;11:1326418. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1326418. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38274536 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaline Water Mitigates Bone Loss in Streptozotocin-Induced Type II Diabetic Rats.Cureus. 2024 May 7;16(5):e59833. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59833. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38846188 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent fasting and bone health: a bone of contention?Br J Nutr. 2023 Nov 14;130(9):1487-1499. doi: 10.1017/S0007114523000545. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Br J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36876592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox Homeostasis and Molecular Biomarkers in Precision Therapy for Cardiovascular Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;13(10):1163. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101163. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

