Dietary fat and carbohydrate affect the metabolism of protein-based high-density lipoprotein subspecies
- PMID: 34907968
- PMCID: PMC8855953
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000809
Dietary fat and carbohydrate affect the metabolism of protein-based high-density lipoprotein subspecies
Abstract
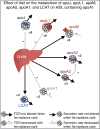
Purpose of review: Dietary fat compared to carbohydrate increases the plasma concentration of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol. However, neither the mechanism nor its connection to cardiovascular disease is known.
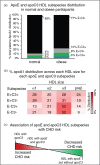
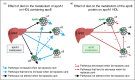
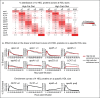
Recent findings: Protein-based subspecies of HDL, especially those containing apolipoprotein E (apoE) or apolipoprotein C3 (apoC3), offer a glimpse of a vast metabolic system related to atherogenicity, coronary heart disease (CHD) and other diseases. ApoE stimulates several processes that define reverse cholesterol transport through HDL, specifically secretion of active HDL subspecies, cholesterol efflux to HDL from macrophages involved in atherogenesis, size enlargement of HDL with cholesterol ester, and rapid clearance from the circulation. Dietary unsaturated fat stimulates the flux of HDL that contains apoE through these protective pathways. Effective reverse cholesterol transport may lessen atherogenesis and prevent disease. In contrast, apoC3 abrogates the benefit of apoE on reverse cholesterol transport, which may account for the association of HDL that contains apoC3 with dyslipidemia, obesity and CHD.
Summary: Dietary unsaturated fat and carbohydrate affect the metabolism of protein-defined HDL subspecies containing apoE or apoC3 accelerating or retarding reverse cholesterol transport, thus demonstrating new mechanisms that may link diet to HDL and to CHD.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Sacks FM, Lichtenstein AH, Wu JHY, et al. . Dietary fats and cardiovascular disease: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017; 136:e1–e23. - PubMed
-
- Mensink RP, Zock PL, Kester AD, Katan MB. Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins: a meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77:1146–1155. - PubMed
-
- Appel LJ, Sacks FM, Carey VJ, et al. . Effects of protein, monounsaturated fat, and carbohydrate intake on blood pressure and serum lipids: results of the OmniHeart randomized trial. JAMA 2005; 294:2455–2464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

