R 0 estimation for COVID-19 pandemic through exponential fit
- PMID: 34908637
- PMCID: PMC8662303
- DOI: 10.1002/mma.7878
R 0 estimation for COVID-19 pandemic through exponential fit
Abstract
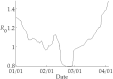
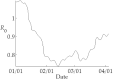
We provide an easy and accurate method for approximating the reproduction number R 0 defined in an SIR epidemic model. At first, we present a formula extracting the exact R 0 in case of constant rates of infection and recovery assumed in an SIR model. Then, we proceed proposing an exponential fitting to various data taken from the real-world epidemics. Certain applications for current COVID outbreak are considered, and figures describing the fluctuation of R 0 in various countries are given.
Keywords: COVID‐19 outbreak; SIR epidemic model; exponential fitting; initial value problem.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Kermack WO, McKendrick AG. Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics—I. Proc R Soc A. 1927;115:700‐721. - PubMed
-
- Beckett SJ, Dominguez‐Mirazo M, Lee S, Andris C, Weitz JS. Spread of COVID‐19 through Georgia, USA. Near‐term projections and impacts of social distancing via a meta population model. 10.1101/2020.05.28.20115642; 2020. - DOI
-
- Medvedev MA, Simos TE, Tsitouras C. Fitted modifications of Runge‐Kutta pairs of orders 6(5). Math Meths Appl Sci. 2018;41:6184‐6194.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
