Orexins: A promising target to digestive cancers, inflammation, obesity and metabolism dysfunctions
- PMID: 34908800
- PMCID: PMC8641057
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i44.7582
Orexins: A promising target to digestive cancers, inflammation, obesity and metabolism dysfunctions
Abstract
Hypothalamic neuropeptides named hypocretin/orexins which were identified in 1998 regulate critical functions such as wakefulness in the central nervous system. These past 20 years had revealed that orexins/receptors system was also present in the peripheral nervous system where they participated to the regulation of multiple functions including blood pressure regulation, intestinal motility, hormone secretion, lipolyze and reproduction functions. Associated to these peripheral functions, it was found that orexins and their receptors were involved in various diseases such as acute/chronic inflammation, metabolic syndrome and cancers. The present review suggests that orexins or the orexin neural circuitry represent potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of multiple pathologies related to inflammation including intestinal bowel disease, multiple sclerosis and septic shock, obesity and digestive cancers.
Keywords: Cancer; G-protein coupled receptor superfamily; Inflammation; Metabolic syndrome; Neuropeptide; Orexin.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors don’t have any conflict of interest.
Figures
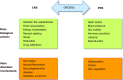
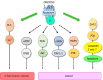

References
-
- de Lecea L, Kilduff TS, Peyron C, Gao X, Foye PE, Danielson PE, Fukuhara C, Battenberg EL, Gautvik VT, Bartlett FS 2nd, Frankel WN, van den Pol AN, Bloom FE, Gautvik KM, Sutcliffe JG. The hypocretins: hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:322–327. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richardson JA, Kozlowski GP, Wilson S, Arch JR, Buckingham RE, Haynes AC, Carr SA, Annan RS, McNulty DE, Liu WS, Terrett JA, Elshourbagy NA, Bergsma DJ, Yanagisawa M. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 1998;92:573–585. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, Fitch TE, Nakazato M, Hammer RE, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. 1999;98:437–451. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, Sinton CM, Yanagisawa M. Polysomnographic characterization of orexin-2 receptor knockout mice. Sleep . 2000;23:A296–A297.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

