Scoping insight on antiviral drugs against COVID-19
- PMID: 34909060
- PMCID: PMC8366046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103385
Scoping insight on antiviral drugs against COVID-19
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 is an ongoing viral pandemic produced by SARS-CoV-2. In light of in vitro efficacy, several medications were repurposed for its management. During clinical use, many of these medications produced inconsistent results or had varying limitations.
Objective: The purpose of this literature review is to explain the variable efficacy or limitations of Lopinavir/Ritonavir, Remdesivir, Hydroxychloroquine, and Favipiravir in clinical settings.
Method: A study of the literature on the pharmacodynamics (PD), pharmacokinetics (PK), safety profile, and clinical trials through academic databases using relevant search terms.
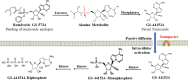
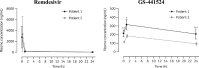
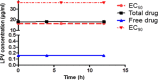
Results & discussion: The efficacy of an antiviral drug against COVID-19 is associated with its ability to achieve therapeutic concentration in the lung and intestinal tissues. This efficacy depends on the PK properties, particularly protein binding, volume of distribution, and half-life. The PK and PD of the model drugs need to be integrated to predict their limitations.
Conclusion: Current antiviral drugs have varying pharmacological constraints that may associate with limited efficacy, especially in severe COVID-19 patients, or safety concerns.
Keywords: Favipiravir; Hydroxychloroquine; Lopinavir; Pharmacodynamics; Pharmacokinetics; Remdesivir; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Remdesivir, Lopinavir/Ritonavir, and Favipiravir for COVID-19 Treatment: A Systematic Review.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Nov 23;14:8557-8571. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S332458. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34849001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Strategies for COVID-19 - A Review of the Most Promising Repurposed Antiviral Drugs.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(7):e160921189260. doi: 10.2174/1871526520666201218151841. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 33342420 Review.
-
A Narrative Review of Antiviral Drugs Used for COVID-19 Pharmacotherapy.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021 Apr-Jun;13(2):163-171. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_498_20. Epub 2021 May 26. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021. PMID: 34349475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and efficacy of antiviral combination therapy in symptomatic patients of Covid-19 infection - a randomised controlled trial (SEV-COVID Trial): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 20;21(1):866. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04774-5. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33081849 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic Effectiveness and Safety of Repurposing Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19: Position Standing in 2021.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 14;12:659577. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.659577. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34220503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse roles of SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Nucleocapsid proteins in EndMT stimulation through the TGF-β-MRTF axis inhibited by aspirin.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 May 28;22(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38807115 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Delivery of Hydroxychloroquine Nanostructured Lipid Carrier as a Potential Treatment of COVID-19.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 28;14(13):2616. doi: 10.3390/polym14132616. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808662 Free PMC article.
-
Repositioned Natural Compounds and Nanoformulations: A Promising Combination to Counteract Cell Damage and Inflammation in Respiratory Viral Infections.Molecules. 2023 May 12;28(10):4045. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104045. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Polysaccharide "Immeran" Activity in Syrian hamsters' Model of SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2024 Mar 9;16(3):423. doi: 10.3390/v16030423. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albariqi Ahmed H., Chang Rachel Yoon Kyung, Tai Waiting, Ke Wei-Ren, Chow Michael Y.T., Tang Patricia, Kwok Philip Chi Lip, Chan Hak-Kim. Inhalable Hydroxychloroquine Powders for Potential Treatment of COVID-19. J. Aerosol. Med. Pulm Drug Deliv. 2021;34(1):20–31. - PubMed
-
- Aleem, A., Kothadia, J., Remdesivir, in StatPearls. 2021, StatPearls Publishing. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
